دور الإضاءة الخلفية في رؤية الآلة في تحسين جودة الصورة
فهم إضاءة الخلفية في رؤية الآلة
في أنظمة الأتمتة الصناعية وفحص الجودة، تلعب إضاءة الخلفية في رؤية الآلة دوراً أساسياً في تمكين التقاط الصور بدقة. وعلى عكس الإضاءة الأمامية أو الجانبية، فإن إضاءة الخلفية تضع مصدر الضوء خلف الجسم، مما يخلق تبايناً قوياً بين هيئة الجسم والخلفية. وهذه الطريقة تكون فعالة بشكل خاص في التطبيقات التي تكون فيها قياس الحواف أو اكتشاف الأشكال أو التعرف على العيوب الصغيرة أموراً ضرورية. ومن خلال الإضاءة من الخلف، يمكن للأنظمة البصرية أن تميز الخصائص بدقة أكبر، حتى في البيئات المعقدة أو ذات السرعة العالية.
لماذا تحسّن إضاءة الخلفية جودة الصورة
تُحسّن الإضاءة الخلفية جودة الصورة بشكل أساسي من خلال زيادة التباين بين الجسم وخلفيته. في العديد من الحالات الصناعية، يمكن أن تُعقّد تحليل الصور الانعكاسات على السطح والظلال والتغيرات في الملمس. تتفادى الإضاءة الخلفية هذه المشكلات من خلال إنشاء خلفية مشرقة وثابتة وعرض الجسم كملامح داكنة وواضحة. تُلغي هذه التقنية العديد من عدم الانتظام التي قد تسببها الإضاءة الأمامية، مما يسمح بتحليل أكثر دقة لكشف الحواف وقياس الأبعاد والتعرف على الأشكال.

التطبيقات عبر الصناعات
تُستخدم الإضاءة الخلفية في رؤية الآلة في صناعات متنوعة، من تصنيع الإلكترونيات إلى تعبئة المنتجات وإنتاج الأدوية. على سبيل المثال:
- فحص الإلكترونيات: تحديد عيوب في مكونات الدوائر المطبوعة أو دبابيس الموصلات.
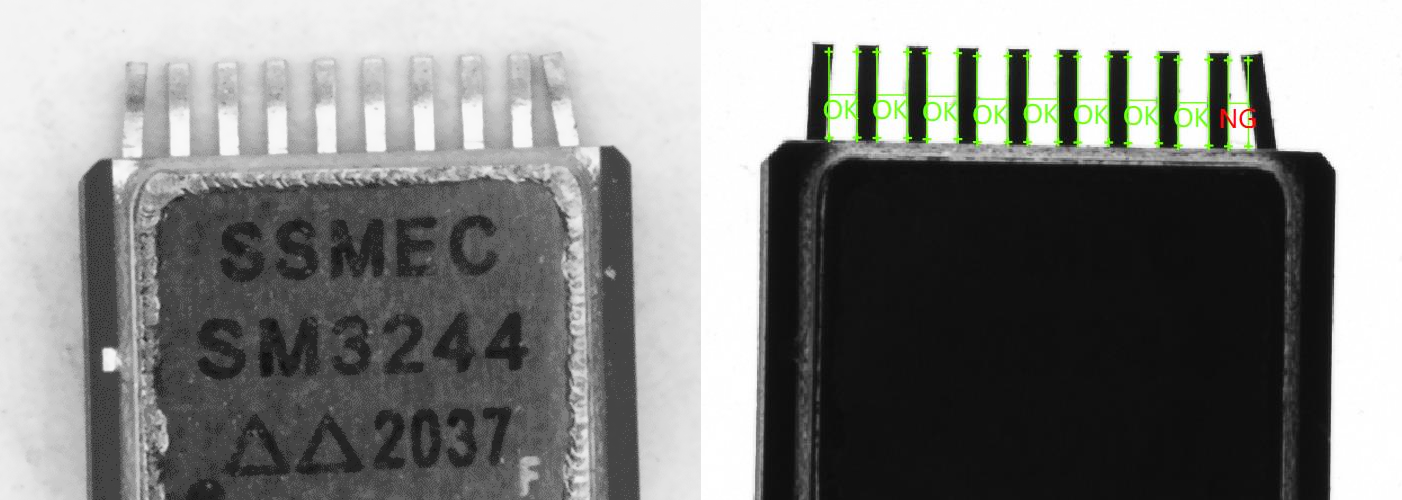
- فحوصات جودة التعبئة: التأكد من أن الختم والملصقات والأشكال تطابق المواصفات بدقة.
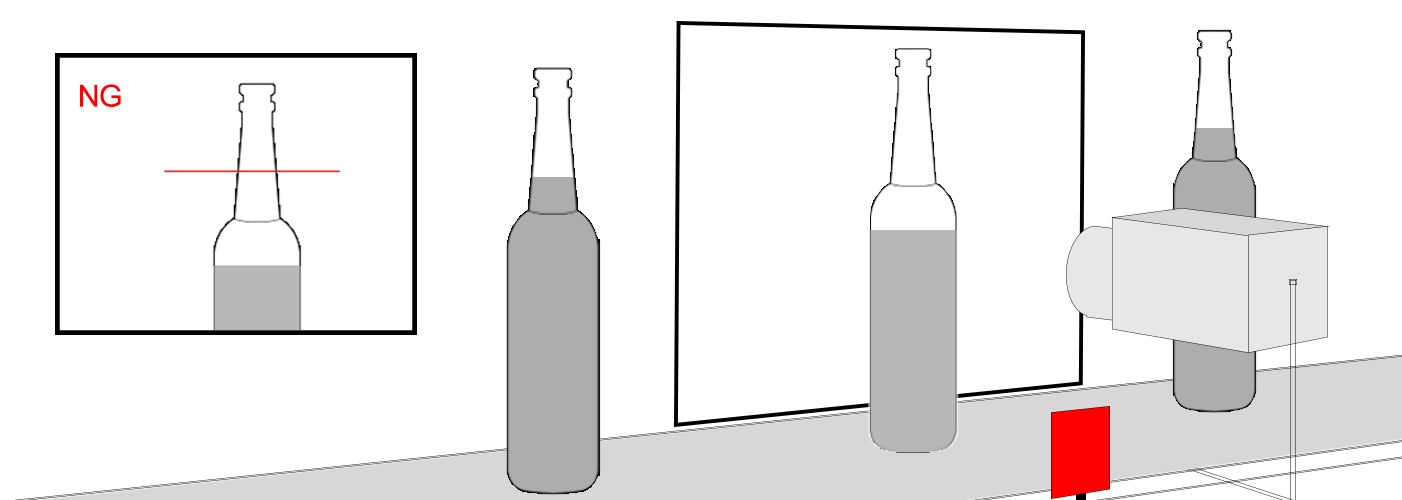
- الصناعات الدوائية: اكتشاف العيوب في الحبوب أو مستويات التعبئة داخل الحاويات الشفافة.
- تفتيش أجزاء السيارات: قياس السدادات، والترسينات، أو المكونات المصممة بدقة.
بفضل توفيره هيئة ظلية واضحة وعالية التباين، يسمح الإضاءة الخلفية للخوارزميات الرؤية الآلية بأداء قياسات دقيقة واكتشاف التغيرات بدقة أكبر.
دمج الإضاءة الخلفية في نظام الرؤية
تعتمد فعالية الإضاءة الخلفية ليس فقط على جودتها ولكن أيضًا على دمجها الصحيح في نظام الرؤية. يجب وضع مصدر الضوء بدقة خلف الجسم، ومحاذاة مع محور العدسة الكاميرا لتوليد هيئة ظلية مثالية. يمكن استخدام مُفَتِّحات الضوء لتخفيف الإضاءة وإزالة التدرجات الحادة، بينما يمكن استخدام العدسات المُوازِية للضوء لتركيزه والحصول على حواف أكثر وضوحًا. بالإضافة إلى ذلك، فإن اختيار العدسة وإعدادات الكاميرا المناسبة أمر بالغ الأهمية لاستكمال فوائد الإضاءة الخلفية.
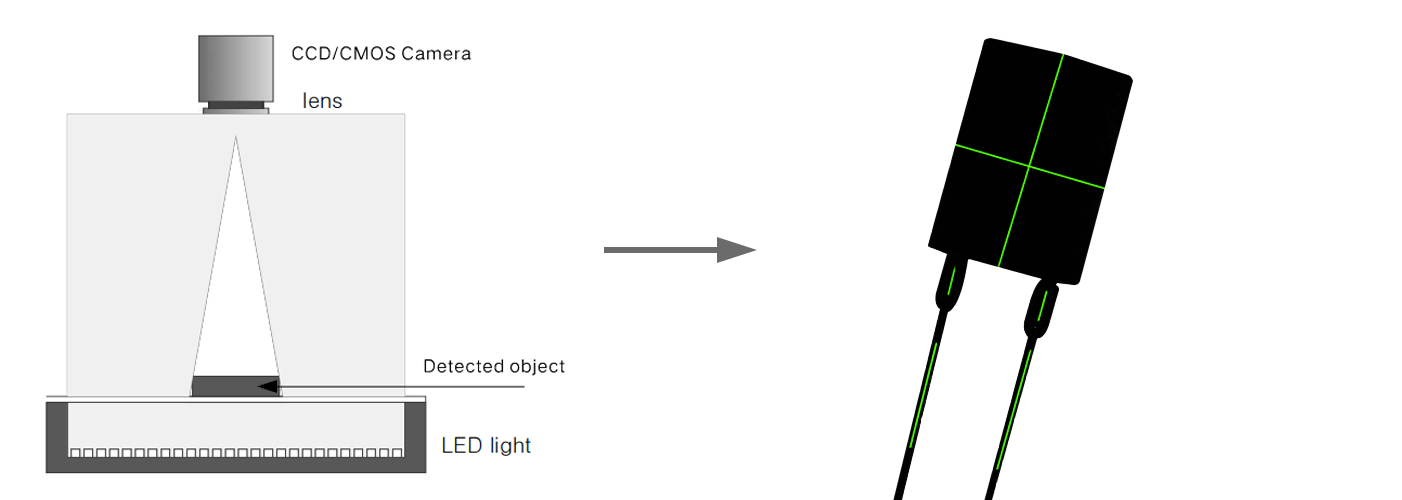
الإضاءة الخلفية مقابل تقنيات الإضاءة الأخرى
بينما تتفوق الإضاءة الخلفية في تحديد الحواف والأشكال، إلا أنها ليست حلاً شاملاً. فالإضاءة الأمامية تكون أفضل لالتقاط تفاصيل السطح، والإضاءة الجانبية هي المثالية لإبراز النسيج. في العديد من أنظمة الرؤية الآلية المتقدمة، تُستخدم مجموعة من تقنيات الإضاءة - مع التبديل الديناميكي بينها ليناسب متطلبات الفحص. ومع ذلك، عندما تكون دقة تحديد الحافة هي الأهم، تظل الإضاءة الخلفية بلا منازع.
التحديات الشائعة وكيفية التغلب عليها
تشمل بعض التحديات المرتبطة بالإضاءة الخلفية ما يلي:
- الوهج أو تسرب الضوء: يمكن تقليل ذلك باستخدام دروع مناسبة أو مصادر ضوء متوازية.
- عدم كفاية السطوع في المجالات الواسعة للرؤية: يمكن أن تعالج هذه المشكلة استخدام إضاءة LED عالية القدرة أو إضاءات خلفية متعددة متزامنة.
- تراكم الحرارة: تساعد إدارة الحرارة بشكل فعال في إطالة عمر الإضاءة الخلفية ذات السطوع العالي والحفاظ على ثبات الأداء.
- من خلال التعاون مع متخصصين ذوي خبرة في إضاءة أنظمة الرؤية الآلية، يمكن تجاوز هذه التحديات لضمان تشغيل موثوق.
التطورات في تقنية الإضاءة الخلفية
تُحسّن الابتكارات الحديثة من فعالية الإضاءة الخلفية وكفاءة استهلاكها للطاقة. تتيح مصفوفات LED عالية الكثافة، وأغشية الانتشار المتقدمة، والتحكم التكيفي في السطوع ضبطًا أكثر دقة لإخراج الضوء. تتكامل بعض أنظمة الإضاءة الخلفية الآن مع برامج الرؤية الآلية، مما يُتيح ضبط السطوع ديناميكيًا استجابةً لبيانات الفحص اللحظية. يُعدّ هذا المستوى من التكيف ذا قيمة خاصة في بيئات الإنتاج ذات أحجام المنتجات أو سرعاتها أو موادها المتغيرة.
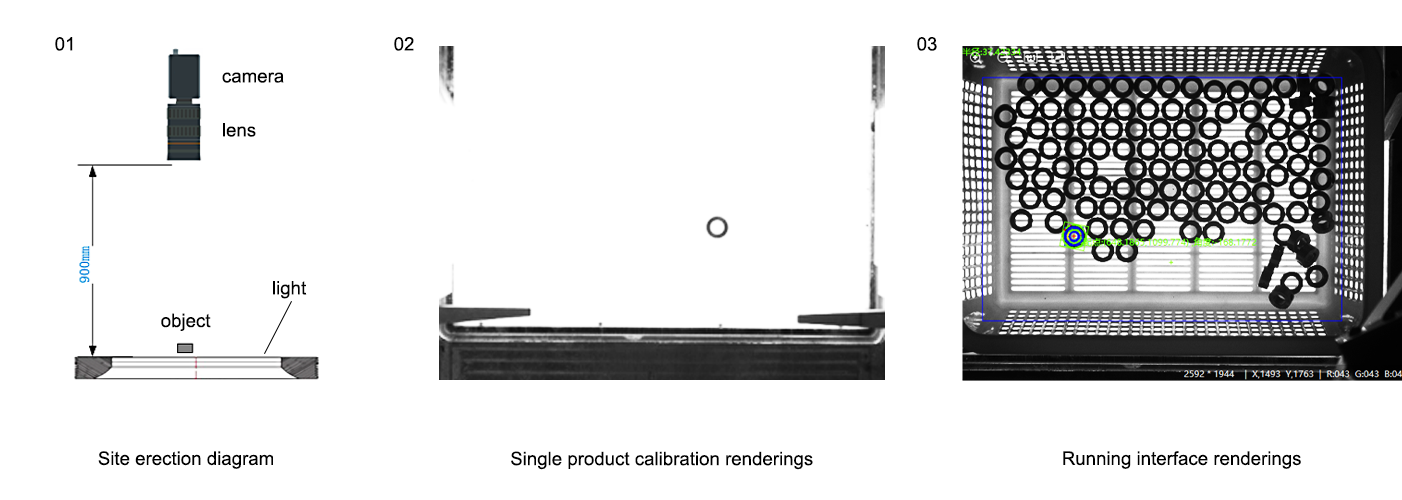
التأثير على أداء النظام ككل
في نظام رؤية الآلة، تتجاوز مهمة الإضاءة الخلفية مجرد إضاءة الجسم. من خلال توفير إدخال مرئي نظيف وثابت، تقلل الإضاءة الخلفية من أخطاء المعالجة، وتقصر من أوقات الفحص، وتحسّن موثوقية النظام. تتطلب الصور ذات التباين العالي جهدًا حاسوبيًا أقل لاكتشاف الحواف والقياسات، مما يمكّن من زيادة سرعة الإنجاز دون التفريط في الدقة. ومع مرور الوقت، يمكن أن تتحول هذه الكفاءة إلى وفورات مالية كبيرة وتحسين في جودة الإنتاج.
خلاصة
إن الإضاءة الخلفية في رؤية الآلة تُعد أداة لا غنى عنها لتحقيق التقاط الصور بدقة عالية في الأتمتة الصناعية. وبفضل توفيرها تباينًا متفوقًا، وتقليل الضوضاء البصرية، وتمكين تكوين صور دقيقة للأحزمة، فإن الإضاءة الخلفية المُصممة بشكل جيد تُحسّن الأداء لأنظمة الرؤية بشكل ملحوظ. سواء في تصنيع الإلكترونيات، أو التعبئة، أو صناعة السيارات، أو إنتاج الأدوية، فإن الإضاءة الخلفية المناسبة تضمن أن تكون عمليات الفحص فعّالة وموثوقة. ومع استمرار تطور تقنيات الإضاءة، فإن إمكانية تحقيق دقة وتكيف أعظم في أنظمة رؤية الآلة لن يتوقف عن التوسع.