BI-Telecentric Lenses: Advantages, Disadvantages, Comparisons and Applications
In the field of machine vision, BI-Telecentric lenses have become the preferred choice for high-precision detection due to their unique optical design that completely eliminates measurement errors from both object and image distance changes, and this article elaborates on their core characteristics, comparisons, and applications.
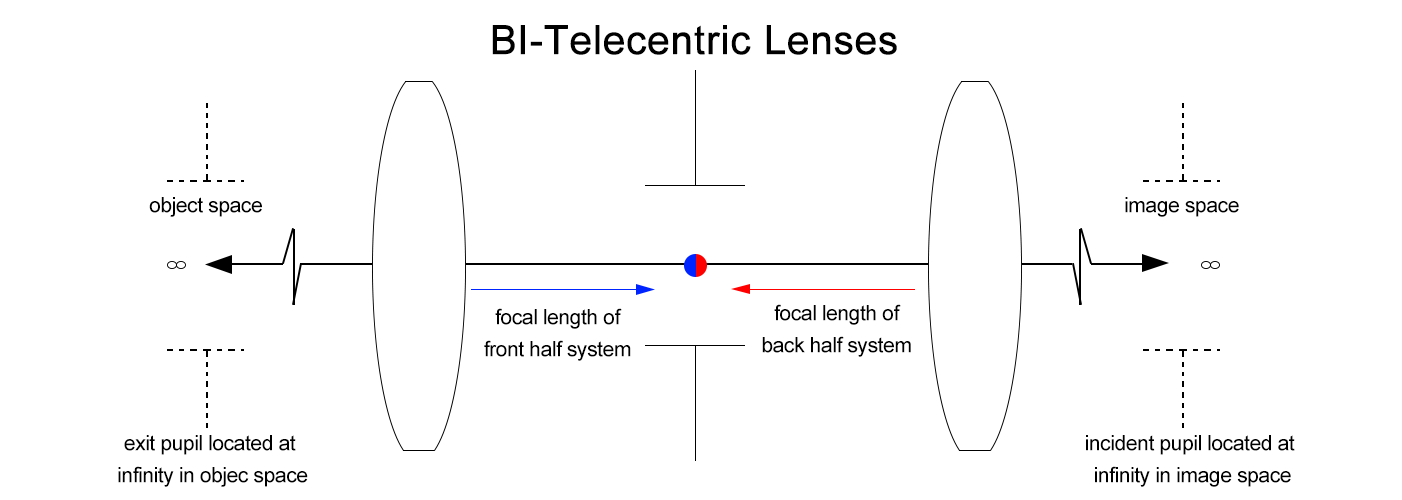
1. What is a BI-Telecentric Lens?
A BI-Telecentric Lens is a high-precision optical lens with chief rays parallel to the optical axis on both the object and image sides, integrating the advantages of single telecentric lenses to keep image size unchanged regardless of distance changes, which is its core difference from other lenses and lays a foundation for ultra-high-precision industrial measurement.
2. Advantages of BI-Telecentric Lenses
Benefiting from their dual-parallel optical path design, BI-Telecentric Lenses have unparalleled advantages in high-precision scenarios, including complete elimination of parallax error, ultra-high micron-level measurement accuracy, ultra-low distortion (≤0.1%), uniform magnification, ultra-wide depth of field, and strong adaptability to reflective or uneven object surfaces.
3. Disadvantages of BI-Telecentric Lenses
The complex dual-parallel optical path design brings limitations to BI-Telecentric Lenses, such as much higher cost than traditional and single telecentric lenses, larger volume and weight, strict dependence on parallel light sources (increasing system cost), and a smaller field of view that limits application in large-size object detection.
4. Comparisons Between BI-Telecentric Lenses and Other Lenses
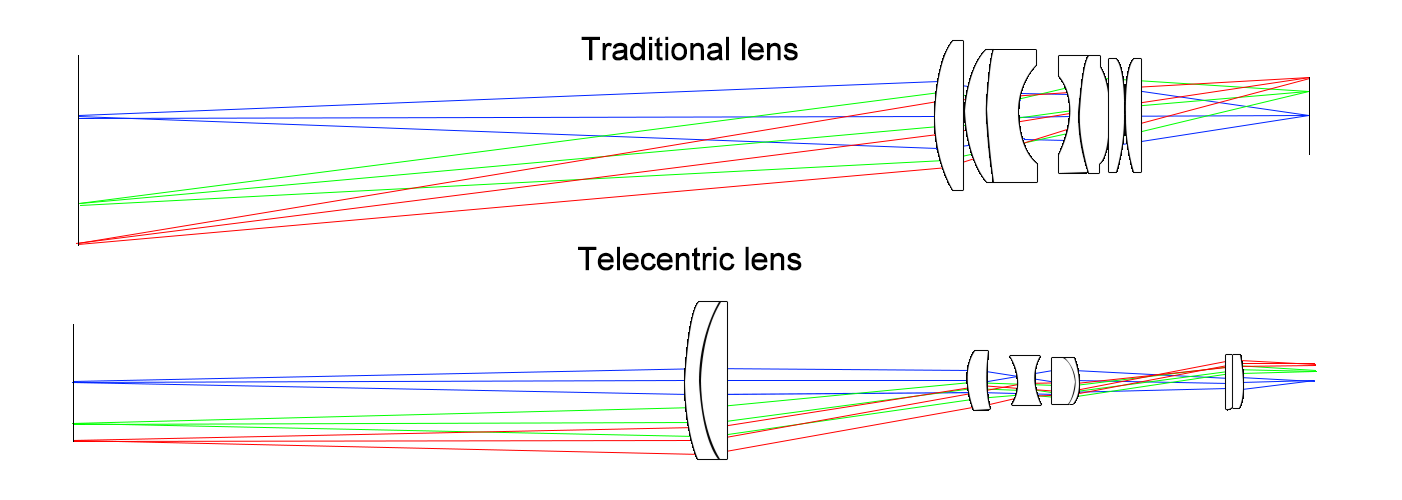
Compared with traditional industrial lenses, BI-Telecentric Lenses are far superior in parallax elimination, accuracy, distortion control and depth of field, while traditional lenses have advantages of low cost and small size for low-precision scenarios; compared with single telecentric lenses, BI-Telecentric Lenses offer more comprehensive precision advantages but are more expensive, making them the optimal choice for high-precision needs.
5. Applications of BI-Telecentric Lenses
With ultra-high accuracy and stable imaging, BI-Telecentric Lenses are widely used in high-precision industrial fields, including electronic manufacturing (component measurement and defect detection), semiconductor industry (wafer and chip precision measurement), mechanical manufacturing (precision part detection), automotive industry (high-precision component inspection), and medical device industry (device size and defect detection).
6. Conclusion
BI-Telecentric Lenses are irreplaceable in high-precision industrial measurement due to their unique advantages, despite limitations like high cost and large size; as industrial automation develops, their application will expand, and future optical technology progress is expected to overcome their current limitations and promote high-precision detection development.