Machine Vision Smart Cameras: Transforming Industrial Production
As a core component of Industry 4.0 and intelligent manufacturing, machine vision smart cameras have become a key driver of efficiency and quality improvement in industrial production—their ability to automate visual tasks, reduce human error, and enable real-time decision-making has made them indispensable across sectors like electronics, automotive, and aerospace, making it critical to explore their practical applications and value in modern factories.
1. Applications of Machine Vision Smart Cameras in Industrial Production
Quality Inspection
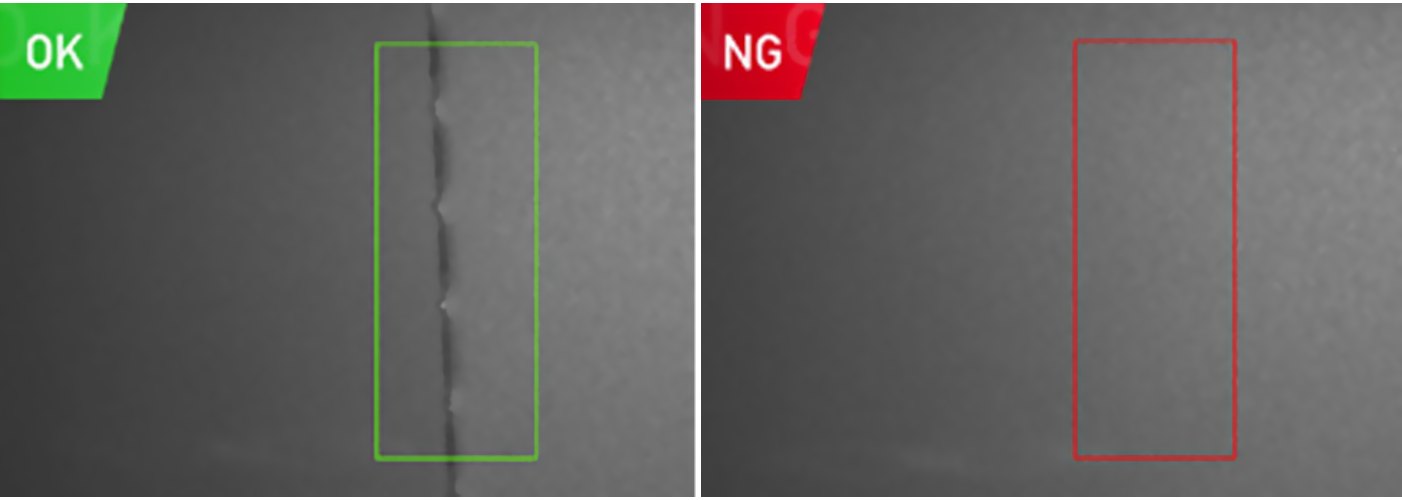
In quality inspection, machine vision smart cameras excel at detecting surface defects such as scratches, cracks, and holes on products ranging from electronic components to automotive parts—unlike manual inspection, they can identify even microscopic flaws consistently, eliminating the risk of human fatigue-related errors. They also verify assembly accuracy, for example, checking if chips are properly soldered on circuit boards or if automotive parts are correctly fitted, ensuring that only qualified products move to the next production stage.
Dimension Measurement
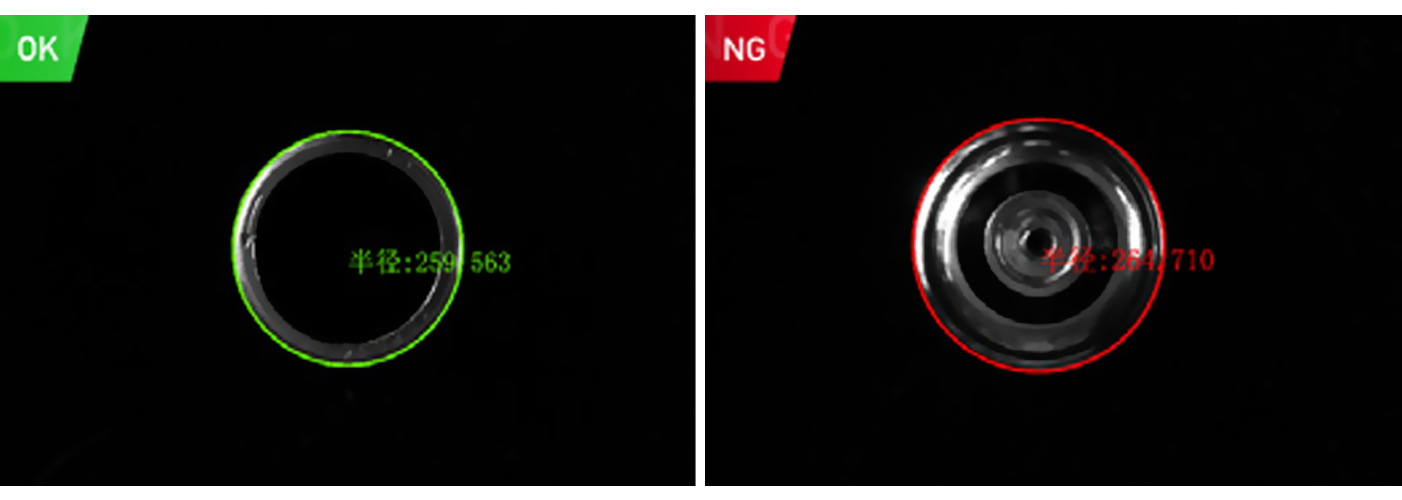
For dimension measurement, these cameras deliver high-precision results in fields like aerospace and precision machining, accurately capturing the size and shape tolerance of small, intricate parts (e.g., engine components) with minimal deviation. They also handle large-scale objects such as construction steel or ship parts, using advanced imaging technology to cover broad surfaces while maintaining measurement accuracy, a task that is both time-consuming and error-prone for manual methods.
Robot Guidance and Navigation
In robot guidance, machine vision smart cameras enable industrial robots to perform precise pick-and-place operations in logistics and electronics manufacturing—by recognizing the position and orientation of items (e.g., smartphone components), they guide robots to grab and place objects without manual intervention, boosting assembly line speed. For mobile robots like AGVs in factories, these cameras provide real-time visual data to help AGVs navigate complex environments, avoid obstacles, and follow optimal paths, ensuring smooth material transportation.
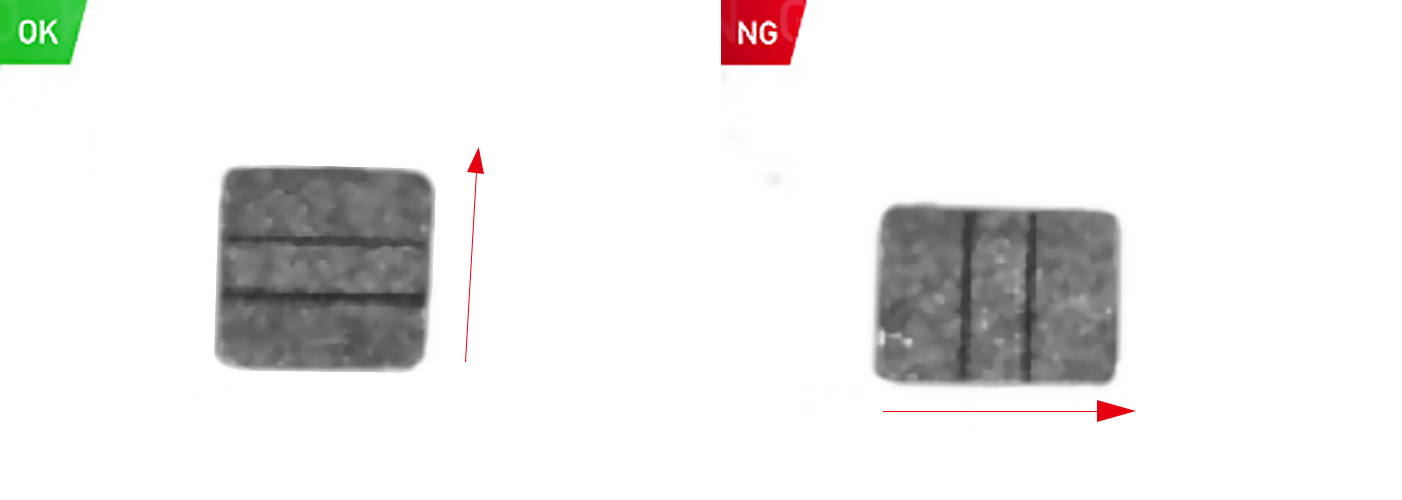

Identification and Traceability
For identification and traceability, the cameras quickly and accurately read barcodes and QR codes on products and packaging, even in harsh industrial conditions (e.g., dusty workshops or low light), enabling fast data collection for inventory management. They also support product tracking throughout the production cycle—by identifying unique visual markers on each product, manufacturers can trace its origin, processing steps, and quality records, which is crucial for recall management and compliance with industry standards.

2. Advantages of Machine Vision Smart Cameras in Industrial Production
Compared to traditional manual processes, machine vision smart cameras offer unmatched precision and accuracy—they can measure dimensions down to micrometers and detect defects invisible to the human eye, ensuring consistent product quality. Their high-speed and real-time processing capability also allows them to keep up with fast-moving production lines, processing hundreds of images per second and providing instant feedback to adjust workflows.
These cameras also enable 24/7 continuous operation, unaffected by factors like fatigue, shift changes, or emotional states, which significantly increases production uptime. Additionally, the data they generate integrates seamlessly with Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) systems, providing manufacturers with insights to optimize production processes, reduce waste, and make data-driven decisions.
3. Challenges and Solutions in the Application of Machine Vision Smart Cameras
One major challenge is complex lighting conditions in factories—glare, shadows, or uneven illumination can distort images, affecting detection accuracy. To address this, manufacturers often pair smart cameras with specialized lighting systems (e.g., coaxial lights, ring lights) that minimize reflections and ensure consistent image quality. Another technical hurdle is meeting ultra-high accuracy requirements in sectors like semiconductor manufacturing, which requires advanced lens technology and AI-driven calibration tools to reduce measurement errors.
Cost-related challenges include high initial investment in camera hardware and software, which can deter small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). Solutions here include leasing options or modular systems that allow gradual upgrades, reducing upfront costs. Long-term maintenance and upgrade costs are also a concern—regular calibration and software updates can be streamlined by partnering with suppliers that offer remote monitoring and maintenance services, lowering operational expenses.
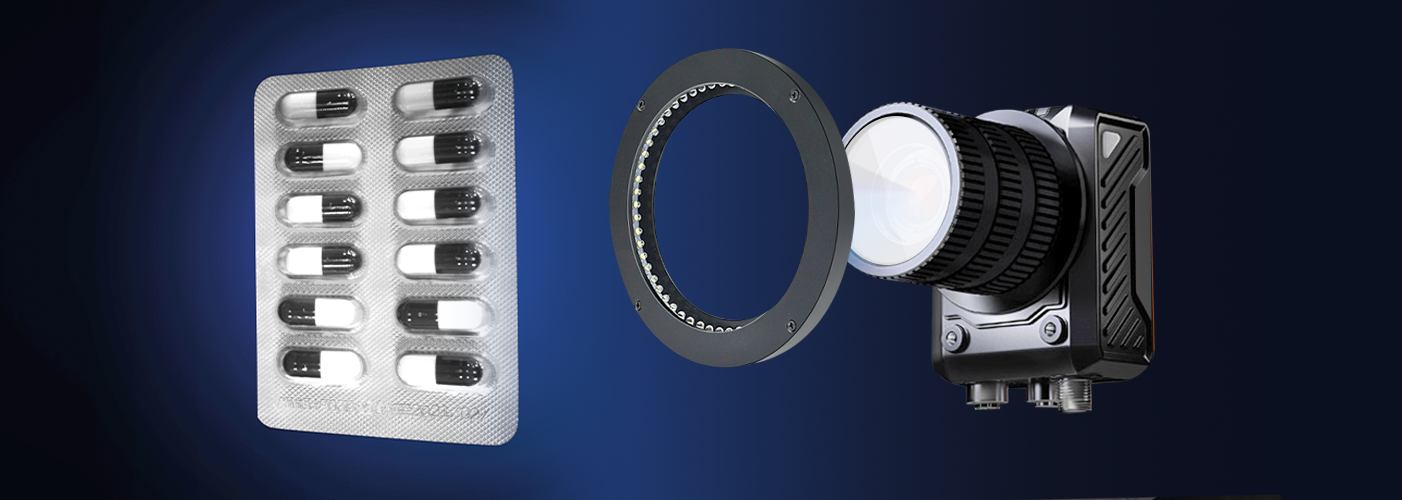

4. Future Trends of Machine Vision Smart Cameras in Industrial Production
The integration of AI and deep learning will be a key trend—smart cameras will increasingly use machine learning algorithms to adapt to new product types automatically, reducing the need for manual programming (e.g., detecting defects in different smartphone models without reconfiguring settings). This will also enable more advanced tasks like predictive maintenance, where cameras analyze subtle visual changes in equipment to forecast potential failures.
Another trend is the development of 3D vision technology, which will allow smart cameras to capture detailed 3D models of complex parts (e.g., engine cylinders), enabling more accurate defect detection and dimension measurement than 2D systems. Miniaturization and integration will also progress—cameras will become smaller and more lightweight, making them suitable for tight spaces (e.g., inside industrial robots) while integrating with other sensors (e.g., temperature, pressure sensors) to provide comprehensive production data.
5. Conclusion
Machine vision smart cameras play a pivotal role in modern industrial production, driving automation, improving quality, and enhancing efficiency across diverse sectors. While they face challenges like lighting complexities and cost barriers, innovative solutions and technological advancements are addressing these issues. Looking ahead, the integration of AI, 3D vision, and miniaturization will expand their capabilities further, making them even more essential for manufacturers aiming to stay competitive in the era of intelligent manufacturing.