Selection of Industrial Cameras
The selection of industrial cameras should be based on specific application scenarios, with a focus on key parameters such as resolution, frame rate, and sensor type. The following are the main points for selection:
1. Clarify Core Requirements
Detection target: It is necessary to clarify the size, details (such as whether to identify tiny defects), and movement state (static or high-speed moving) of the detected object.
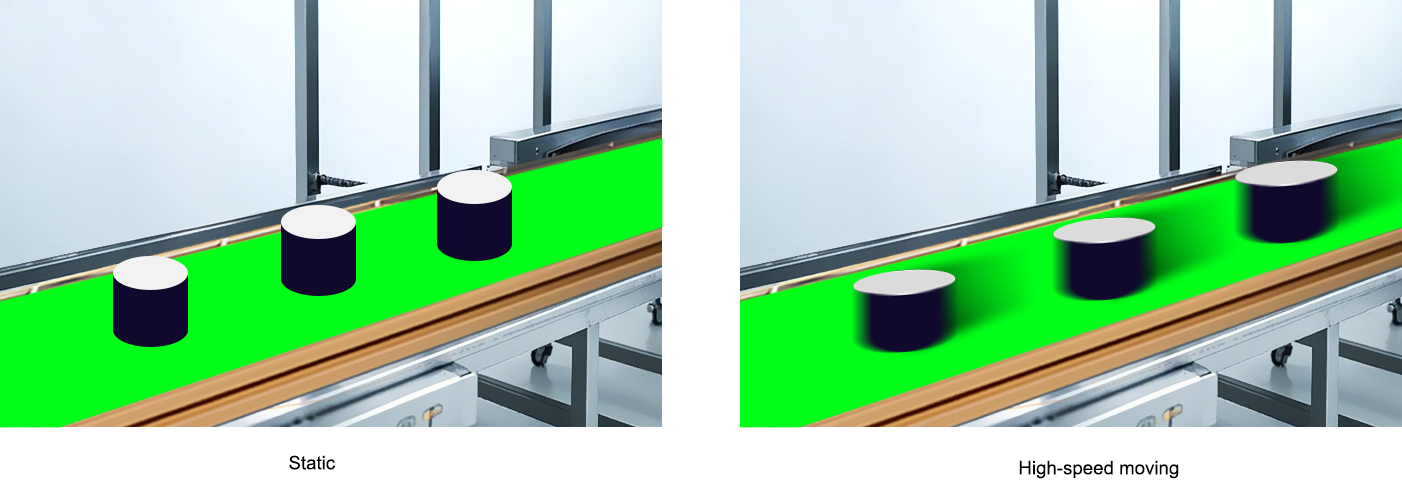

Application scenarios: For example, it is used for defect detection, dimension measurement, OCR recognition, positioning guidance, etc. Different scenarios have significantly different requirements for camera parameters.
2. Selection of Key Parameters
Resolution
It needs to meet the requirement of detecting the smallest details. Reference formula: Resolution = Detection field of view range / Minimum detection accuracy.
Example: If the detection field of view is 100mm and the minimum accuracy is 0.1mm, the resolution should be at least 1000 pixels (100/0.1).
Frame rate
It depends on the moving speed of the object and must ensure that clear images are captured during movement.
High frame rates (such as above 30fps) are required for high-speed movement scenarios (such as rapid transmission in assembly lines).
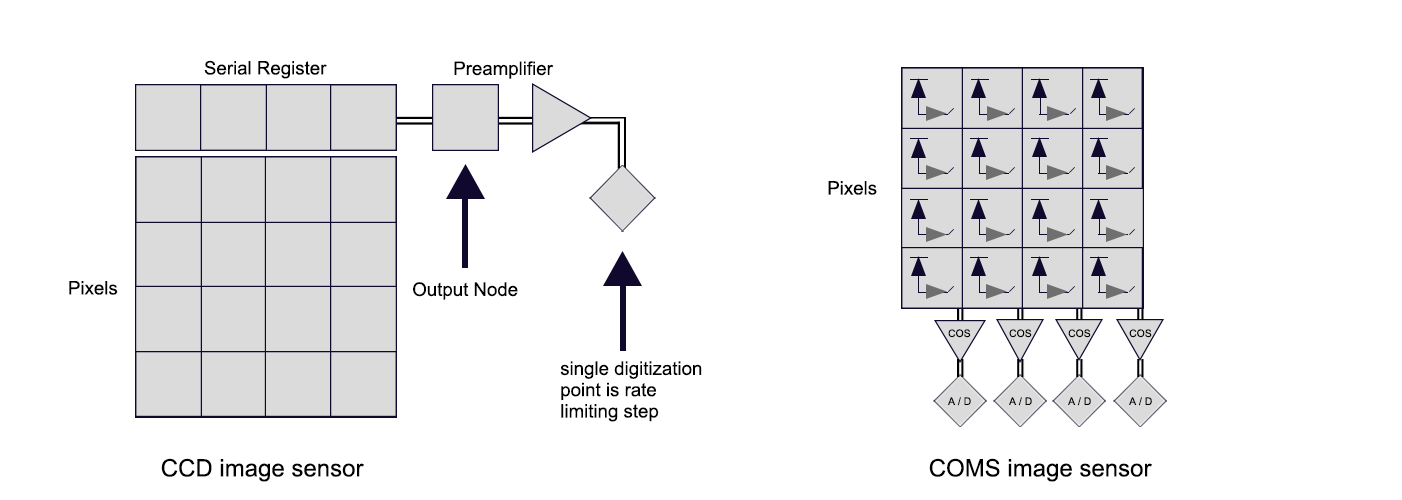
Sensor type
CCD: It has good imaging quality and high sensitivity, suitable for low-light environments, but the cost is relatively high and the frame rate is relatively low.
CMOS: It has low cost, high frame rate, and low power consumption, suitable for high-speed scenarios, and is widely used in mainstream industrial cameras.
Spectral response
Ordinary cameras are suitable for visible light; for special scenarios (such as infrared temperature measurement, fluorescence detection), cameras with corresponding spectral responses (such as infrared cameras, ultraviolet cameras) should be selected.
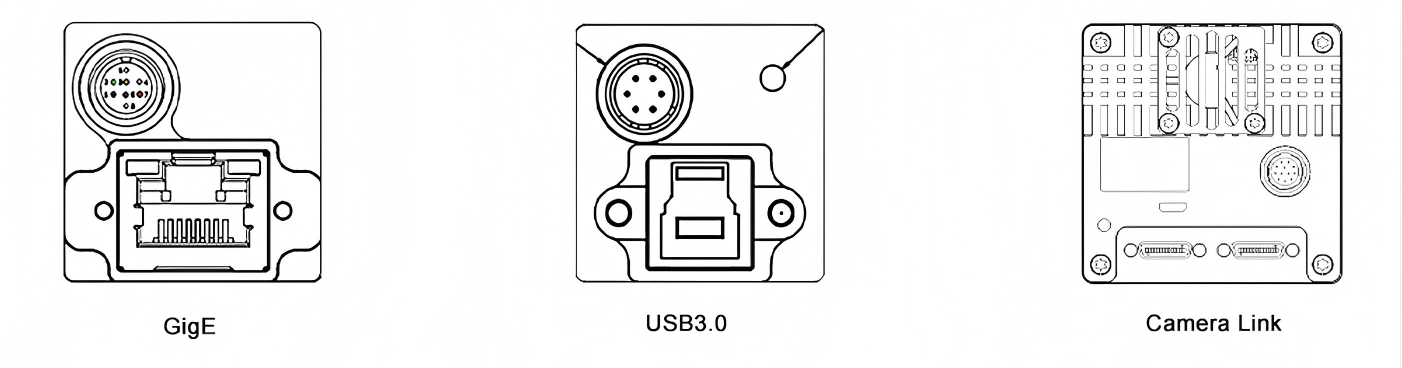
Interface
Common interfaces: GigE (Gigabit Ethernet, with long transmission distance, suitable for multi-camera synchronization), USB3.0 (high-speed and convenient, suitable for short distances), Camera Link (high bandwidth, suitable for ultra-high resolution/frame rate scenarios).
3. Other considerations
Working environment: Factors such as temperature, humidity, and vibration should be considered, and cameras with industrial-grade protection (such as IP67) should be selected.
Software compatibility: Ensure that the camera is compatible with image processing software (such as Halcon, OpenCV).
Cost budget: On the premise of meeting performance requirements, balance the cost and avoid over-configuration.
In summary, for selection, it is necessary to first clarify the detection target and scenario, then match core parameters such as resolution, frame rate, and sensor accordingly, while taking into account the interface, environmental adaptability, and cost.