The Ultimate Guide to Choosing Telecentric Lenses for Machine Vision Success
Why Telecentric Lenses Matter in Machine Vision
Imagine a world where your machine vision system captures images so precise that every measurement is flawless, every defect is caught, and every process runs smoothly. That’s the power of telecentric lenses—a game-changer in industries like manufacturing, robotics, and quality control. But here’s the catch: not all telecentric lenses are created equal, and choosing the right one can feel like navigating a tech maze. Whether you’re a seasoned engineer or new to machine vision, this guide will break down everything you need to know about selecting telecentric lenses. Ready to unlock crystal-clear imaging and boost your system’s performance? Let’s dive in!
What Are Telecentric Lenses and Why Should You Care?
Telecentric lenses are specialized optical tools designed for precision imaging in machine vision applications. Unlike standard lenses, they maintain consistent magnification regardless of an object’s distance from the lens, eliminating perspective errors and ensuring accurate measurements. This makes them ideal for tasks like inspecting tiny electronic components or measuring parts on a production line.
Why should you care? Because the right telecentric lens can:
Improve Accuracy: Deliver distortion-free images for precise measurements.
Enhance Efficiency: Streamline quality control by reducing errors.
Boost Reliability: Ensure consistent results, even in high-speed setups.
But choosing the wrong lens can lead to blurry images, inaccurate data, or costly reworks. Let’s explore how to pick the perfect one.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting Telecentric Lenses
Selecting a telecentric lens isn’t just about picking the most expensive option—it’s about matching the lens to your specific application. Here are the critical factors to consider:
1. Understand Your Application Needs
Every machine vision task is unique. Are you inspecting flat surfaces, like circuit boards, or 3D objects, like mechanical parts? Do you need high-resolution imaging for tiny details or a wider field of view for larger components? Define your goals:
Inspection Type: Surface defects, dimensional measurements, or alignment.
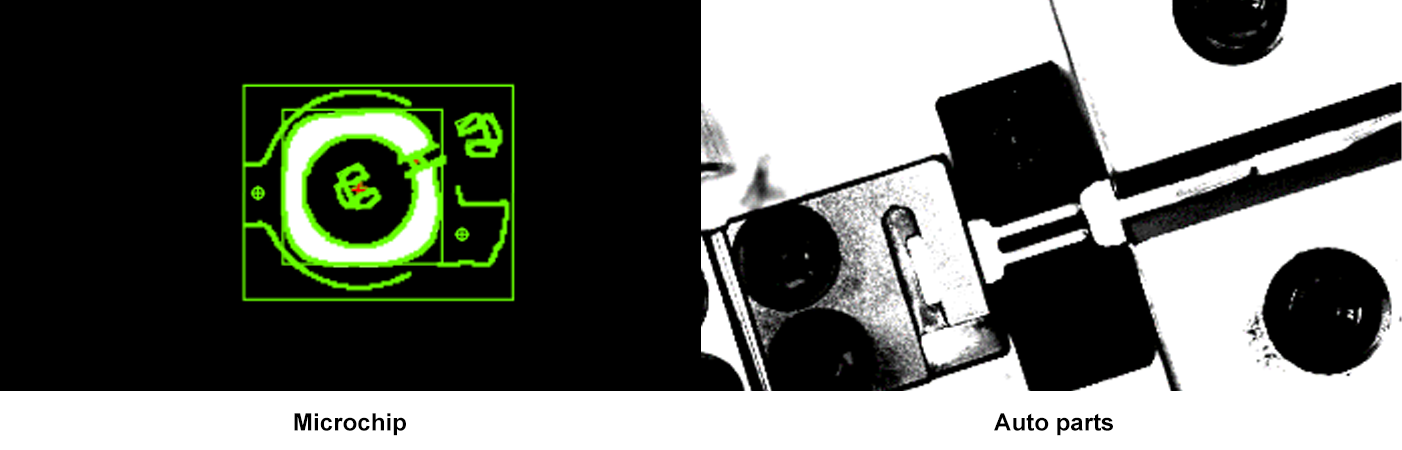
Object Size: Small (e.g., microchips) or large (e.g., automotive parts).
Working Distance: How far is the object from the lens?
For example, inspecting a 10mm-wide microchip requires a high-magnification lens with a small field of view, while a 100mm-wide car part demands a larger field and lower magnification.

2. Choose the Right Telecentric Lens Type
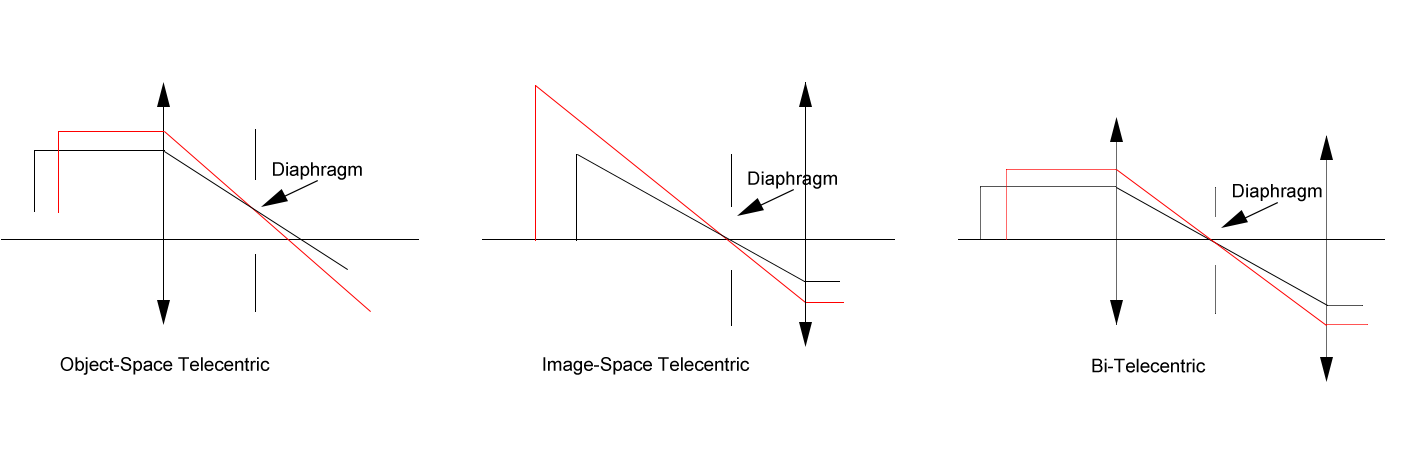
Telecentric lenses come in three main flavors:
Object-Space Telecentric: Parallel light rays on the object side, ideal for precise measurements of flat objects.
Image-Space Telecentric: Parallel rays on the camera side, great for reducing sensor-related distortions.
Bi-Telecentric: Parallel rays on both sides, offering maximum precision but at a higher cost.
For most applications, object-space telecentric lenses strike the best balance of performance and affordability. Bi-telecentric lenses are overkill unless you’re working on ultra-precise tasks like semiconductor inspection.
3. Match the Lens to Your Camera Sensor
Your lens and camera sensor must work in harmony. Key considerations include:
Sensor Size: Ensure the lens’s image circle covers your camera’s sensor (e.g., 1/2”, 2/3”, or full-frame).
Resolution: Match the lens’s resolution to your camera’s pixel count. A 5MP camera needs a lens that can resolve fine details without pixelation.
Mount Type: Common mounts like C-mount or F-mount must align with your camera.
Mismatching these can lead to vignetting (dark corners) or wasted resolution. Check your camera’s specs before shopping.
4. Evaluate Field of View (FOV) and Magnification
The field of view determines how much of your object the lens can capture, while magnification controls how large it appears. To calculate:
FOV = Sensor Size / Magnification
Example: A 1/2” sensor (6.4mm wide) with 0.5x magnification gives a 12.8mm FOV.
If your object is 10mm wide, you’d need a lens with an FOV of at least 10mm and enough magnification to resolve critical details. Too small an FOV crops your image; too large wastes resolution.
5. Consider Depth of Field (DOF)
Depth of field is the range of distances where objects remain in sharp focus. Telecentric lenses often have a limited DOF due to their design, so:
For flat objects (e.g., printed circuit boards), a shallow DOF is fine.
For 3D objects (e.g., machined parts), choose a lens with a deeper DOF or adjust your setup to keep the object within the focus range.
6. Don’t Ignore Illumination
Lighting is critical for machine vision, and telecentric lenses often require specific setups:
Telecentric Illuminators: These provide parallel light to match the lens’s optics, reducing shadows and enhancing contrast.
Coaxial vs. Backlighting: Coaxial lighting is great for reflective surfaces, while backlighting highlights edges.
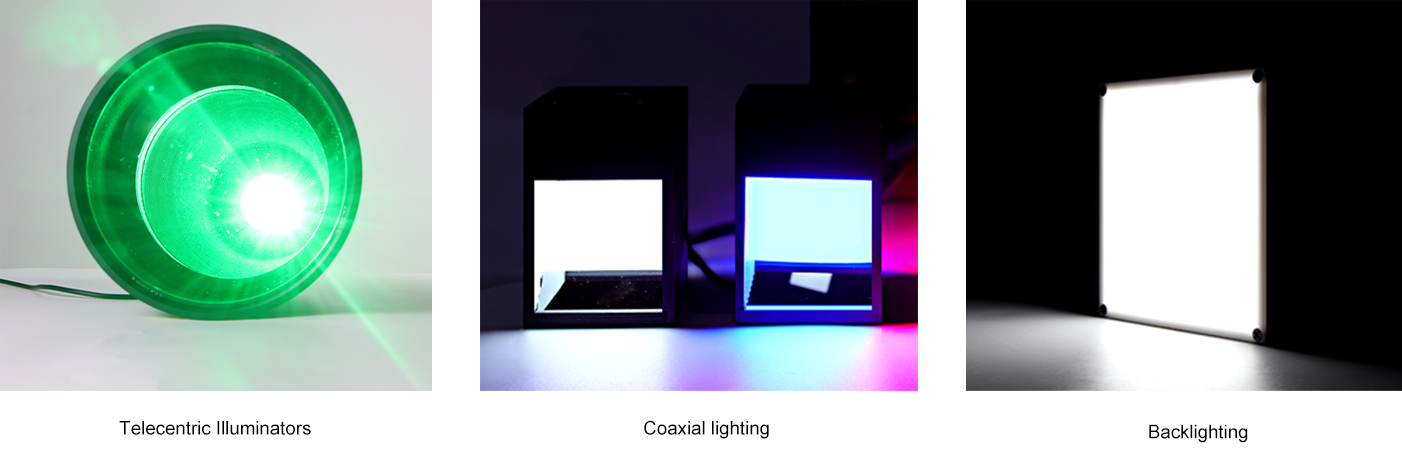

Test your lens with your lighting setup to ensure compatibility and avoid surprises.
7. Budget vs. Performance
Telecentric lenses range from a few hundred to thousands of dollars. While premium lenses offer superior optics, mid-range options often suffice for standard applications. Balance cost with performance by prioritizing must-have features (e.g., magnification) over nice-to-haves (e.g., ultra-low distortion).
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Overlooking Sensor Compatibility: A high-end lens on a low-res camera is like putting racing tires on a bicycle—wasted potential.
Ignoring Working Distance: If your lens can’t fit in your setup’s space constraints, you’re stuck.
Skipping Tests: Always test the lens with your actual setup. Specs on paper don’t always translate to real-world performance.
How to Test and Validate Your Choice
Once you’ve shortlisted a lens, test it:
Set Up a Mock Environment: Use your actual object, camera, and lighting.
Check Image Quality: Look for sharpness, distortion, and consistency across the FOV.
Measure Accuracy: Verify measurements against known standards.
Consult Suppliers: Many vendors offer demo units or technical support to ensure a good fit.
Find Your Perfect Telecentric Lens Today
Choosing the right telecentric lens doesn’t have to be daunting. By understanding your application, matching the lens to your camera, and testing thoroughly, you can unlock the full potential of your machine vision system. Ready to take the next step? Explore top telecentric lens suppliers, request a demo, or consult with a machine vision expert to find the perfect fit for your needs. Don’t let poor optics hold you back—invest in precision and watch your efficiency soar!
Got questions or need help narrowing down options? Contact the HIFLY team to obtain personalized advice. Let’s make your vision system shine!