Machine Vision Lens Types Explained: Fixed, Telecentric, Zoom
Fixed Focal Length Lenses: The Foundation of Stability and Clarity in Machine Vision
Consistent Magnification, Minimal Distortion, and High MTF Performance
Industrial imaging gets much better results with fixed focal length lenses because they stay stable even when working distances change. These lenses keep magnification within ±0.05%, which is pretty impressive considering how sensitive some applications can be. The optical design isn't complicated either, so distortion stays below 0.1%. That matters a lot for accurate measurements in metrology work. When it comes to image quality metrics, these lenses score over 0.8 on the MTF scale at 50 line pairs per millimeter. What does all this mean? Sharper edges and features that are easier to recognize reliably. Zoom lenses just don't match this kind of performance consistency in most industrial settings.
|
Performance Metric |
Fixed Lens |
Zoom Lens |
|
Distortion Range |
<0.1% |
0.3%-1.2% |
|
MTF Consistency |
>0.8 |
0.6–0.75 |
|
Calibration Drift |
Negligible |
High |
Ideal Use Cases: High-Speed Inspection and Repeatable Metrology Tasks
These lenses work really well in places where things need to be checked quickly, such as when looking at semiconductor wafers. The way they're built means they can take consistent pictures even when moving at over 500 parts per minute. When it comes to measuring things accurately, these lenses cut down on errors below 1 micrometer because there's no need to keep adjusting the focus. That saves money too. A study from the Ponemon Institute back in 2023 found that companies saved around $740,000 every year just on the labor costs related to recalibrating equipment. Plus, the build quality is tough enough to handle temperature changes and vibrations, which makes them essential tools for checking car parts during assembly or ensuring medical devices meet quality standards.
Telecentric Lenses: Precision Measurement Through Orthographic Projection
Eliminating Perspective Error for True-Scale Imaging Across Depth
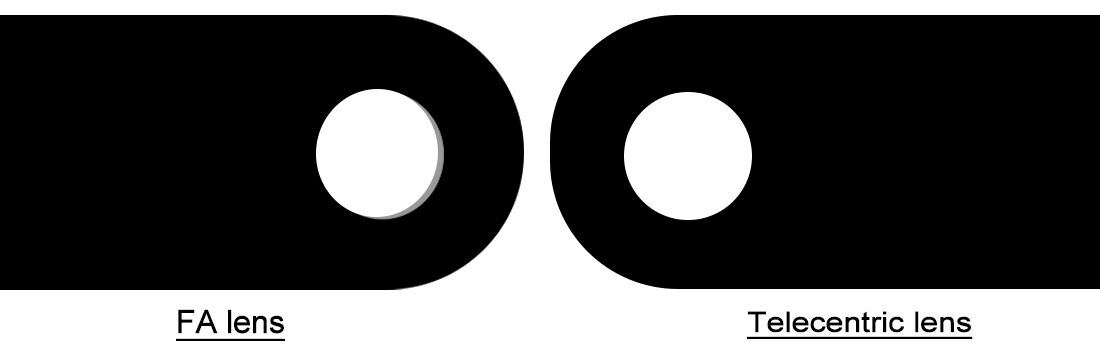
Telecentric lenses work differently from regular optical systems because they use what's called orthographic projection. Basically, these lenses catch light rays that run parallel to each other and hit the image sensor at right angles. The big advantage here is that it gets rid of those pesky perspective distortions which mess up measurements when parts move forward or backward. Take a look at something simple like a round hole in metal. Through normal camera lenses, if the part tilts even a little bit, that hole looks oval instead of round. But with telecentric imaging, the hole stays perfectly circular no matter how it sits relative to the lens. And this matters a lot for checking exact hole sizes in manufactured parts. Research indicates regular setups can be off by as much as 3 percent without proper correction, while telecentric options hit sub pixel level accuracy even when there are plus or minus 5 mm changes in depth. What makes this so valuable is that the magnification stays exactly the same whether the object is close or farther away. That consistency is why manufacturers rely on them for measuring things like how thick edges are or how far apart pins sit on connectors, something regular lenses just can't handle reliably.
|
Distortion Type |
Standard Lens Effect |
Telecentric Correction |
|
Perspective Error |
±2.8% at 5° tilt |
< 0.1% variation |
|
Magnification Shift |
Up to 15%/mm depth |
< 0.1%/mm |
Real-World ROI: How Telecentric Lenses Reduce Rework and Calibration Frequency
Telecentric solutions cut down on operational costs quite a bit when dealing with high precision work because they stop perspective errors right at the beginning. Factories that measure tiny electronic parts see about 40 percent fewer bad readings getting thrown out as waste, plus around 60% less time spent fixing calibration issues once they switch to telecentric lenses. Why does this happen? Well, these special optics don't get messed up by changes in depth or weird edge distortions that usually mess with measurements and force regular readjustments. Pair them with good quality fixtures and what you get is a solid measurement system that keeps working accurately through thousands upon thousands of production cycles without needing anyone to step in and fix things. This makes all the difference for important jobs such as checking if medical devices meet specs or aligning those microscopic chips in semiconductors.
Zoom Lenses: Balancing Flexibility and Performance in Dynamic Machine Vision Applications
Parfocal Design and Motorized Control for Adaptive Field-of-View Adjustment
Zoom lenses today can adjust their field of view while keeping everything in focus thanks to something called parfocal stabilization. This matters a lot on robotic assembly lines where objects keep moving at different distances from the camera. The motorized controls mean operators don't have to constantly readjust settings when changing magnification levels. According to Vision Systems Journal last year, this saves about 15% off inspection times which adds up over time. When checking products on conveyor belts that never stop moving, these lenses follow parts as they pass by even when their position changes relative to the camera angle. What makes them work so well? Built-in systems that constantly check and correct focus automatically, cutting down those annoying pauses between scans that slow down production lines.
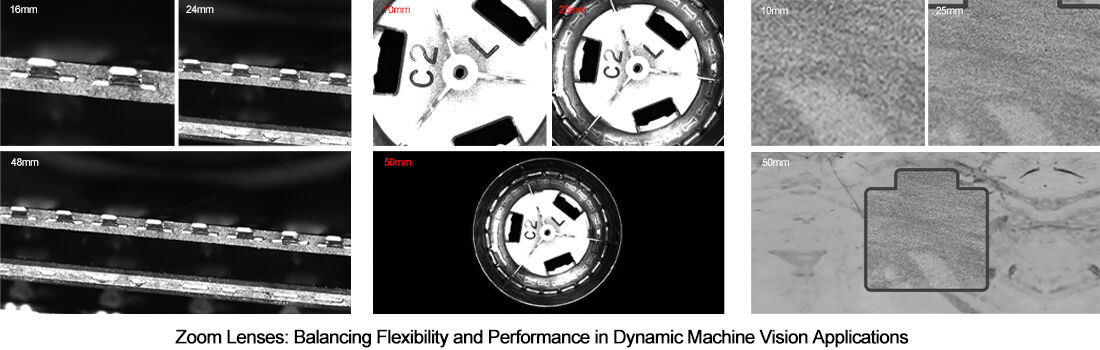
Resolution vs. Versatility Trade-Offs: When Zoom Adds Value Without Compromising Accuracy
While fixed lenses offer maximum MTF ratings, modern zooms achieve comparable clarity through advanced optical stabilization. Key considerations include:
- Resolution thresholds: Zoom optics now deliver consistent >120 lp/mm resolution across focal ranges
- Operational economics: Reduced hardware changeovers cut calibration labor by 30%
- Error mitigation: Multi-position inspections avoid blind spots in PCB defect detection
Leading manufacturers report 99.2% inspection accuracy when deploying zoom lenses for flexible tasks like mixed-product packaging verification. This versatility avoids the traditional resolution compromise, making them ideal for dynamic facilities handling diverse production batches.
Ready to Choose the Right Machine Vision Lens Type?
The appropriate lens type depends on your priorities: stability (fixed), precision (telecentric), or flexibility (zoom). By matching lens characteristics with your application's speed, measurement requirements, and product variety, you'll achieve consistent inspection results.
For customized guidance on fixed, telecentric, or zoom lenses, including their compatibility with your camera system, collaborate with a provider having proven industrial experience. HIFLY's 15 - year expertise covers all three lens types and integrated machine vision solutions, ensuring alignment with your production needs. Contact us today for a no - obligation consultation to optimize your lens selection.