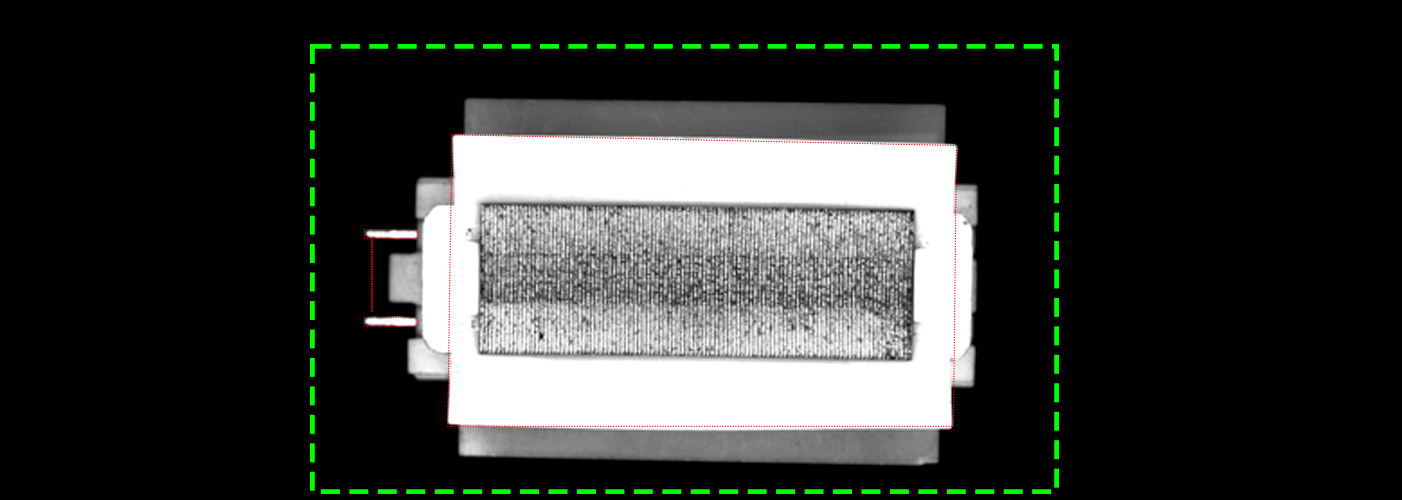
Decoding Industrial Camera Vision: A Deep Dive into Inspection Principles
Industrial cameras are the eyes of machine vision, and understanding their core principles is key to optimizing performance. This article breaks down the fundamental technology behind industrial camera vision, helping engineers and enthusiasts alike grasp the inner workings and fine-tune their systems for success.
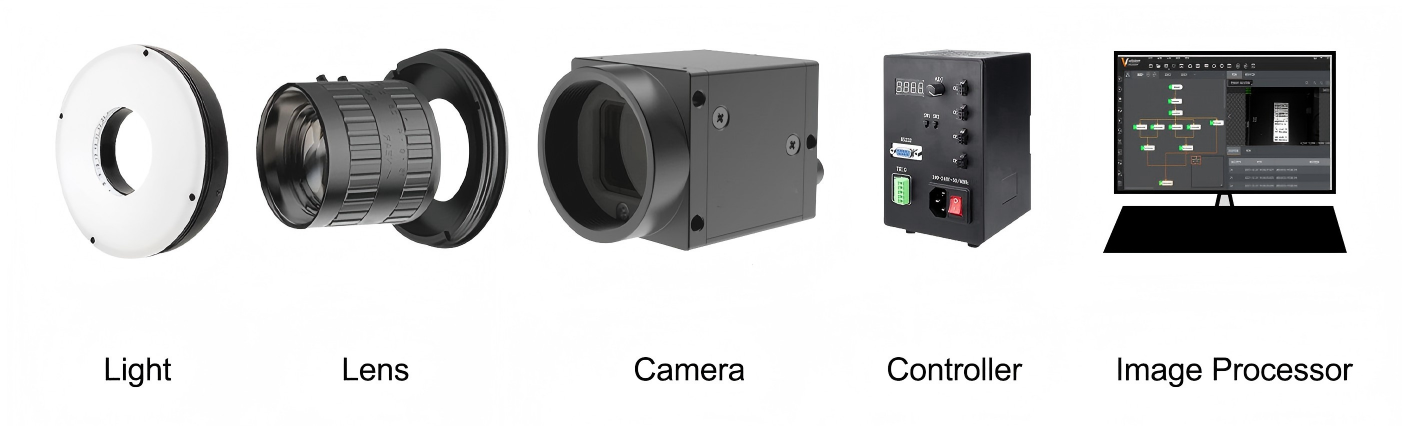
1. The Core Components of an Industrial Camera
Before we dive into the principles, let's understand the essential building blocks:
Optical System: The lens is the light-gathering heart. It's crucial to select a lens that matches the application's field of view, depth of field, and resolution. For example, a 5-megapixel camera requires a lens that can resolve fine details down to the pixel size.
Sensor: The CMOS or CCD sensor converts light into electrical signals. Key metrics include Quantum Efficiency (QE), which should ideally be above 60% for optimal light conversion, and Dynamic Range, which should be over 70dB to handle a wide range of light intensities.
Image Processor: This component handles tasks like Bayer interpolation, noise reduction, and color correction, using algorithms such as a 3x3 matrix to balance white levels.

2. Core Principles of Industrial Camera Vision
Once the image is captured, these advanced principles come into play to extract meaningful data:
Feature Extraction: Algorithms like the Canny operator for edge detection or Normalized Cross-Correlation (NCC) for template matching are used to locate specific targets with sub-pixel precision, often reaching an accuracy of 0.1px.
Distortion Correction: To ensure measurement accuracy, distortion is corrected using calibration methods. This calculates radial and tangential distortion coefficients (k1,k2,p1,p2) to keep measurement errors within ±0.05mm.
Motion Compensation: For moving objects, it's essential to prevent blur. This is achieved by adjusting exposure time based on the object's speed (e.g., an exposure time of ≤500μs for an object moving at 1m/s) and using a global shutter.
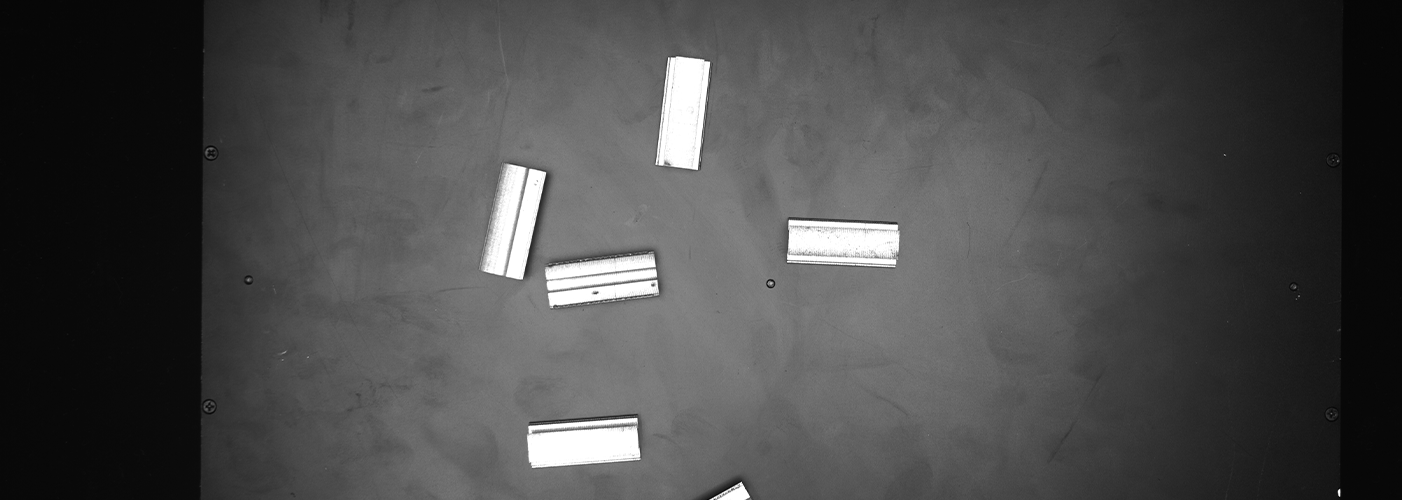

3. Practical Applications of Industrial Camera Systems
These principles are put to use across various industries:
Dimensional Measurement: By calibrating pixels to a real-world scale (e.g., 1px = 0.02mm), these systems can perform highly accurate measurements with a repeatability of ±1μm.
Defect Detection: Using deep learning models like ResNet18, industrial cameras can classify surface scratches and other defects with over 99.5% accuracy.
Robotic Guidance: Through multi-point calibration, these systems can guide robots by translating camera coordinates to the robot's coordinate system with minimal error, often less than 0.1°.