Function and Application of Frame Grabbers in Machine Vision
Machine vision technology is widely used in industrial production inspection, healthcare, transportation, and other fields to help achieve automation and intelligence. The entire machine vision system can be divided into two main modules: image acquisition and image processing. The frame grabber serves as the interface between the image data acquisition part and the processing part, playing a crucial role.
In a machine vision system, the image acquisition part mainly consists of an industrial camera, industrial lens, and lighting system, while the image processing part is realized by image processing software. The frame grabber can be understood as the interface between the industrial camera (video source) and the computer (software). The images acquired by the frame grabber are supplied to the computer or other processors for processing.
I. Principle of Frame Grabbers
First, the specific portion of the real world "seen" by the camera and optical system serves as an optical signal. Then, the CCD or CMOS chip converts the optical signal into an electrical signal. The camera outputs the video signal in a specific format or protocol to the frame grabber. Each pixel independently expresses the light intensity in the form of a Gray Level. These light intensity values are transferred from the matrix of the CCD or CMOS chip and stored in a matrix data structure in memory; the frame grabber is the intermediary for this transfer.
II. Common Parameters of Frame Grabbers
1. A/D Conversion: Frame grabbers can convert analog signals into digital signals, playing a vital role in the image acquisition work of the entire machine vision system. This analog-to-digital conversion performed by the frame grabber in a machine vision system is called A/D conversion, and the corresponding component that implements the conversion is called an A/D converter.
2. Sampling Rate: The sampling rate reflects the speed and capability of the frame grabber in processing images. During image acquisition, attention must be paid to whether the frame grabber's sampling rate meets the requirements.
3. On-board Frame Buffer (Resolution): This determines the maximum pixel array the grabber can support, reflecting its resolution performance, i.e., the maximum camera resolution it can support.
4. Number of Transmission Channels: The ability of the grabber to simultaneously acquire images from multiple cameras. In practical applications, sometimes multiple vision systems need to operate simultaneously to ensure certain production efficiency. Therefore, to meet the needs of system operation, the frame grabber needs to perform A/D conversion on multiple cameras simultaneously. Common transmission channel options for grabbers on the market currently include single-channel, dual-channel, quad-channel, etc.
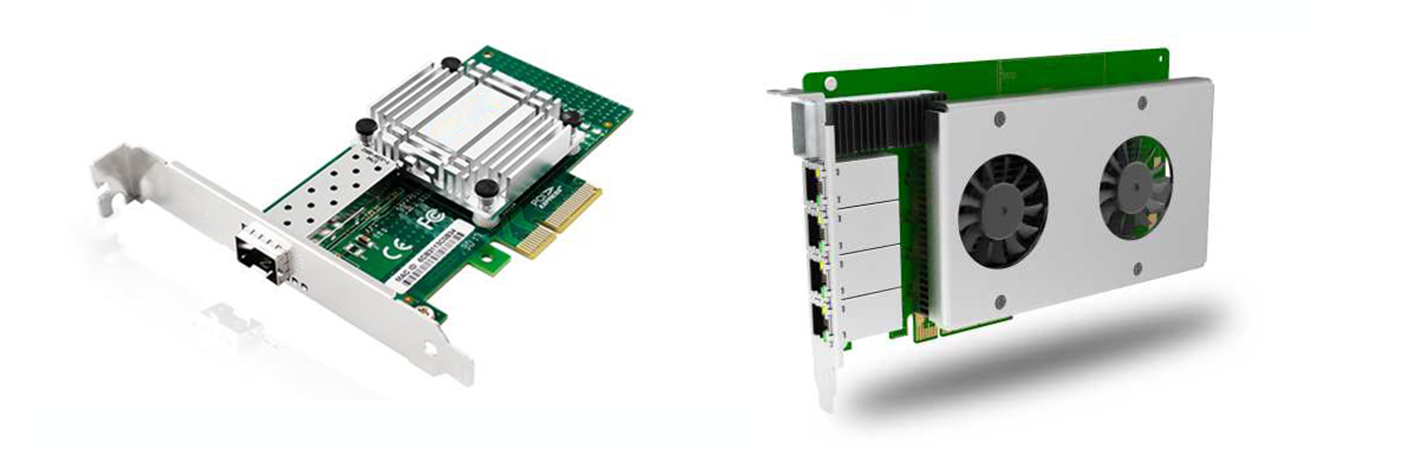

III. Classification of Frame Grabbers
1. Based on Input Signal Type: Analog frame grabbers and digital frame grabbers. Commonly mentioned GigE cards and USB frame grabbers are types of digital frame grabbers.
2. Based on Function: Grabbers with purely acquisition functions and grabbers with integrated image processing functions. With the continuous development of image processing algorithms, image workstations, GPU technology, and smart cameras, the survival space for grabbers with integrated image processing functions is shrinking, and their image processing functions are becoming increasingly singular.
IV. Selection of Frame Grabbers
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Frame Grabber:
1. Signal Interface Type: The video signal interface (type) of the camera and the frame grabber must match: analog signals connect to analog frame grabbers; digital signals connect to digital frame grabbers. There are analog signal interfaces and digital signal interfaces. Analog signal interfaces include BNC, RCA (phono connector), S-video. Digital signal interfaces include CameraLink, Gigabit Ethernet (GigE), CoaXPress (CXP), CLHS, USB 3.0 & 2.0, etc.
2. Sampling Frame Rate: The data sampling frequency of the grabber ≥ the data output frequency of the camera. The requirement that the grabber's data sampling frequency must satisfy can be calculated as follows:
For Analog Grabbers: Point Frequency ≥ 1.2 * R * FPS
For Digital Grabbers: Point Frequency ≥ Camera Point Frequency
Note: R is the camera's resolution, FPS is the camera's frame rate.
3. Software Development Kit (SDK): The selected frame grabber should have a stable, simple, easy-to-use, powerful, and portable SDK. Furthermore, the product line should be well-established to facilitate upgrades.