How To Improve The Inspection Accuracy In Machine Vision System ?
In practical applications, unstable elements in machine vision inspection systems can significantly impact detection accuracy and efficiency. What factors influence the precision of a vision system? Here are the 5 key aspects:
- Resolution Of Industrial Cameras
First, let's discuss the camera resolution. Every image is composed of pixels—the denser the pixels, the clearer the image. Since vision systems rely on pixel calculations to perform tasks, high resolution is the first step toward high precision.
For example, If an image corresponds to a 30 mm × 20 mm area and the camera resolution is 3000 × 2000 (6 megapixels), each pixel represents 0.01 mm. With a 20-megapixel camera (5400 × 3600 resolution), the same field of view achieves a pixel size of 0.005 mm.
Thus, camera resolution has a direct and significant impact on image precision. Choosing a high-resolution camera is essential.
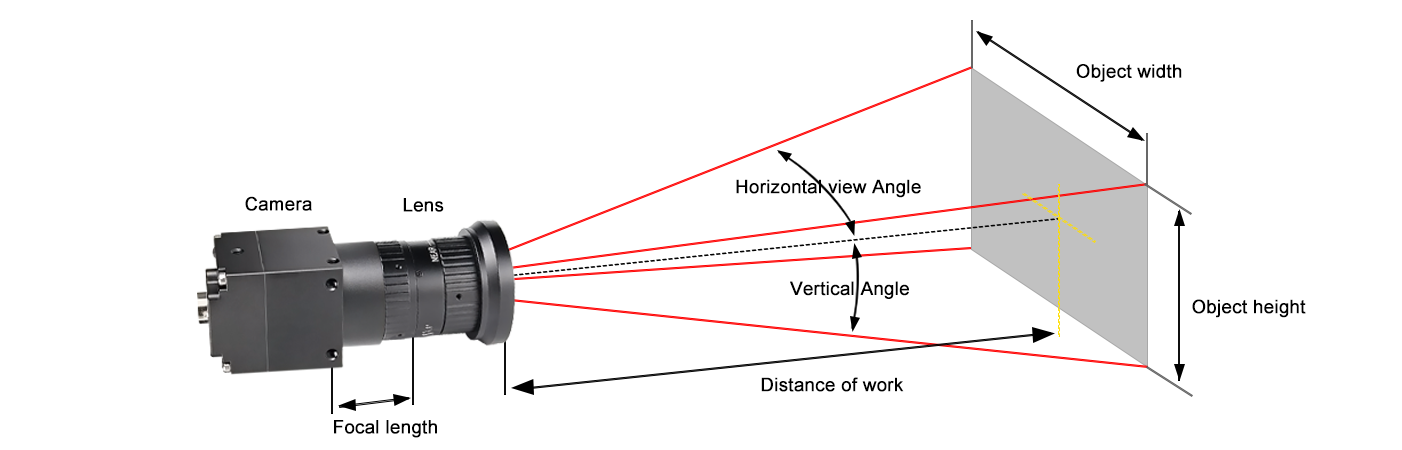
- Field of View (FOV)
After selecting a camera, the field of view is also critical. A larger FOV increases the size of the actual object per pixel, reducing precision. This is why high-precision applications often use smaller FOVs to maximize pixel utilization.
- Lighting Techniques
Lighting plays a vital role in ensuring reliable accuracy. For dimensional measurements, backlighting is typically used. Light shines upward from beneath the product, creating a black silhouette with sharply defined edges.
Below are the 4 types of the backlight.
- Bottom-emitting backlights
- Side-emitting backlights
- Collimated backlights
- Telecentric collimated lights
For high-precision measurements, telecentric collimated light (paired with telecentric lenses) is ideal. It ensures near-vertical illumination, enhancing edge clarity and contrast for higher accuracy.
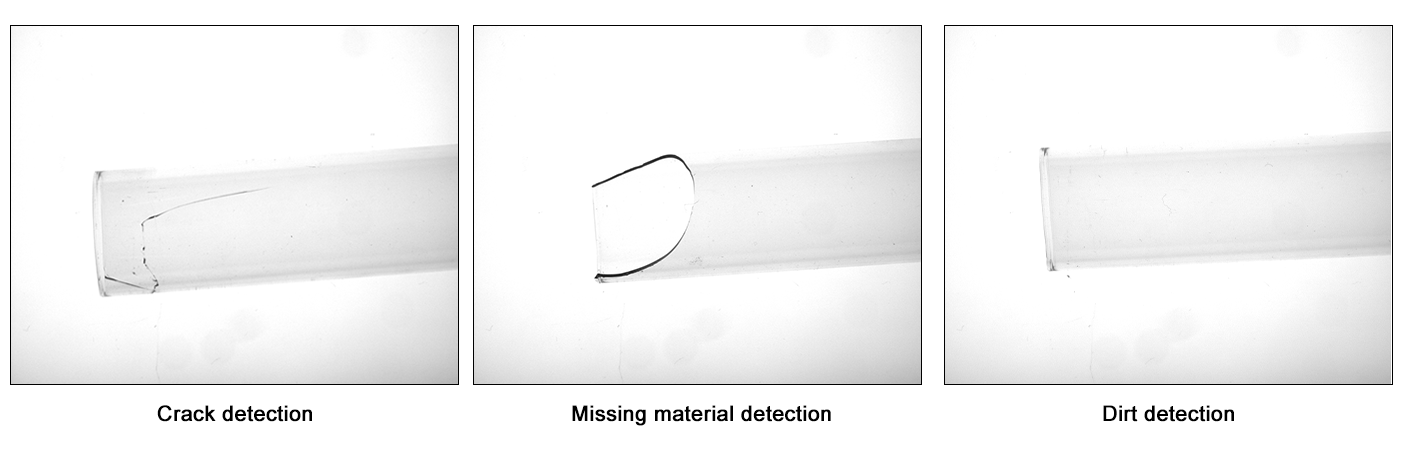

- Type Of Industrial Lenses
Industrial lenses fall into two main categories: FA lenses (standard industrial lenses) and telecentric lenses. Due to their optical design, telecentric lenses eliminate distortion and magnification errors caused by inconsistent object-to-lens distances. For precision measurement, dual-sided telecentric lenses are mandatory.
- Algorithm Software
Even with excellent hardware, software algorithms are critical. For example:
- Line detection accuracy typically fluctuates within 1–2 pixels.
- Arc/diameter measurements can achieve 0.2–1 pixel accuracy.
Advanced algorithms from leading brands can even subdivide a single pixel into 100 subpixels for ultra-fine calculations.
Beyond these five factors, external variables like vibration, temperature fluctuations, and part positioning must be addressed. To account for uncertainties, multiply the calculated pixel accuracy by 2–3 for a realistic final value.