Is A Higher Frame Rate Always Better for Industrial Cameras?
The acquisition speed of an industrial camera, also known as the frame rate, refers to the number of image frames it can capture per second. In machine vision systems, do you think that the higher the camera's frame rate, the better its dynamic performance? Actually, this is incorrect. The frame rate of an industrial camera only indicates the degree of the camera interface and image compression. The higher the interface transmission speed and the smaller the image compression, the higher the frame rate will be. However, this does not directly affect dynamic performance.
What parameter determines the dynamic performance of an industrial camera? In fact, It is exposure time. Exposure time refers to the duration during which the shutter must remain open to project light onto the photosensitive surface of the sensor. For industrial cameras, exposure time is the interval from when the shutter opens until it closes, affecting the brightness of the pixels, typically measured in milliseconds. Frame rate, on the other hand, is the number of image frames that can be fully read out within a unit of time. During this period, objects can leave an image on the imaging surface. Exposure time is determined by need; there is no such thing as good or bad exposure times, only what is needed. The setting for exposure time depends on the sensitivity of the sensor and the illumination on the photosensitive surface.
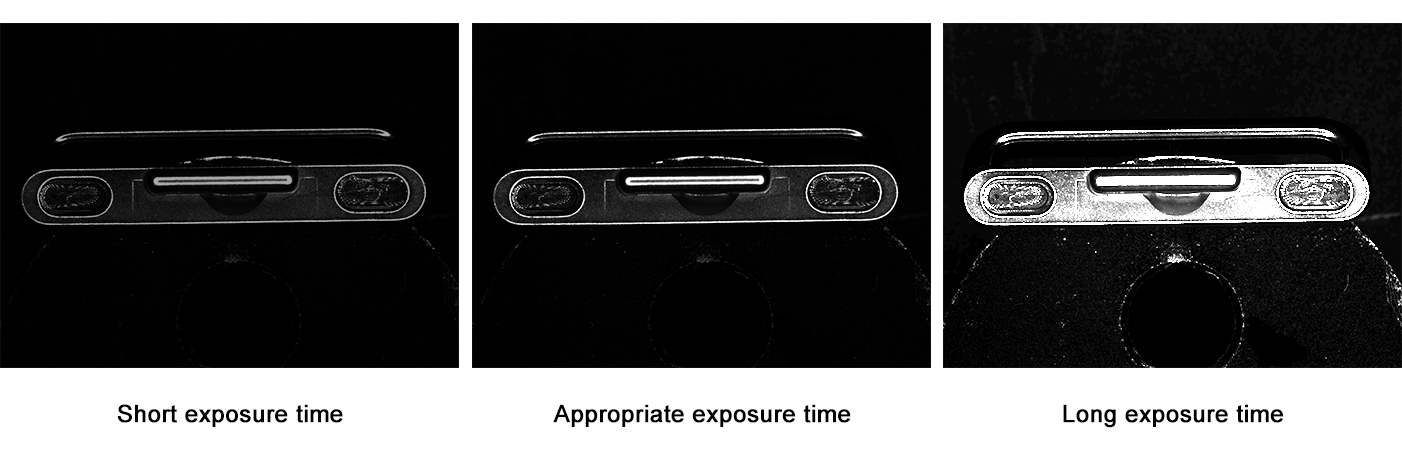
If the exposure time is long, more light will enter, making it suitable for poor lighting conditions. A shorter exposure time is better for good lighting conditions. The longer the exposure time, the brighter the image; conversely, the shorter the exposure time, the darker the image. In situations with poor external lighting, it is generally required to extend the exposure time (for example, night scenes).

Line scan cameras all use row-by-row exposure, with options for fixed line frequency and external trigger synchronization. The exposure time can align with the line cycle or be set to a fixed duration. Area scan cameras offer several common methods such as frame exposure, field exposure, and rolling line exposure. Industrial cameras typically provide external trigger image acquisition functionality.
The shorter the exposure time, the faster the shutter speed of an industrial camera. Currently, most industrial cameras can achieve an exposure time as fast as 1 microsecond. However, with a shorter exposure time, images may become partially or even completely black, so this has certain requirements for the light source and the size of the camera's sensor. In high-speed scenarios, a high-brightness light source and a large-pixel Sensor industrial camera are typically used to capture dynamic scenes.
For dynamic scenes, high frame rates can bring smoother visual effects. For example, when shooting sports events or wildlife, high frame rates can help us capture fast-moving objects, making the footage more vivid. Additionally, high frame rates can be used to create special visual effects, such as slow-motion replays.
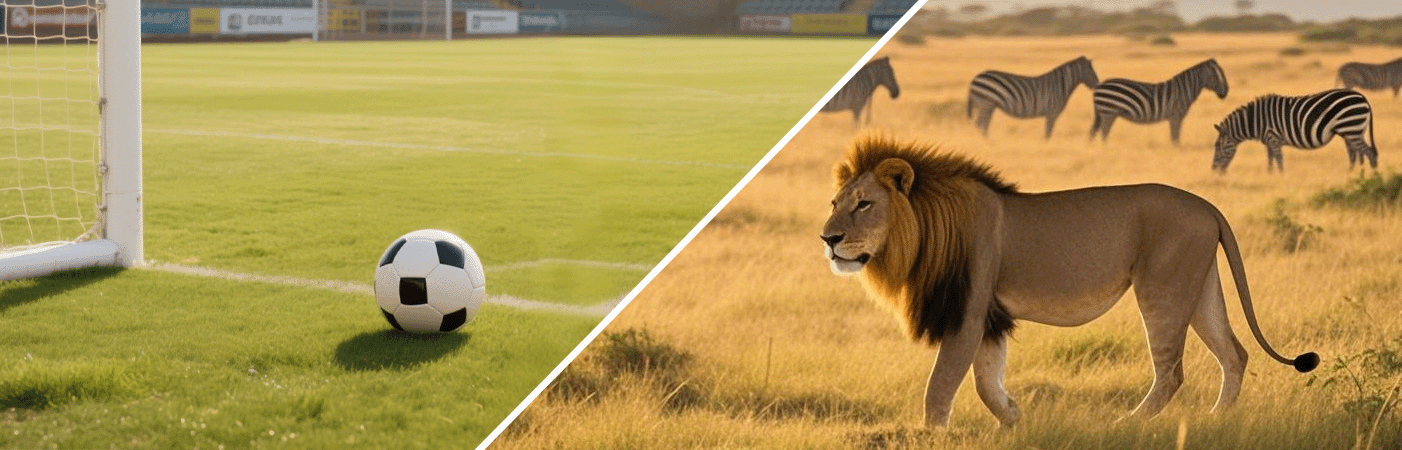

However, high frame rates are not always necessary. For static scenes, low frame rates may be more appropriate. Low frame rates can reduce image noise and blur, enhancing the clarity of the picture. Additionally, low frame rates help save storage space as they generate smaller file sizes.
So how to choose the frame rate of industrial camera?
1. Clarify the Purpose: First, clearly define your shooting needs. Are you capturing high-speed motion scenes or static landscapes? Do you aim for the finest detail or smooth dynamic effects? Different needs require different frame rates. For instance, when shooting high-speed motion scenes, it is recommended to choose a higher frame rate, such as 60FPS or higher, to ensure more details are captured.
2. Consider device compatibility: Make sure your camera, computer, and monitor all support the frame rate you choose. Otherwise, even if your camera can capture a high frame rate, it won't display well on other devices
3. Balancing Performance and Storage: High frame rates mean larger file sizes and higher storage requirements. When selecting a frame rate, it's important to balance the camera's performance, storage capacity, and post-processing capabilities. Ensure your device can handle high frame rate shooting without being hindered by storage issues.
4. Understand formats and codecs: Different video formats and codecs support frame rates differently. It is important to know whether the format and codec you are using support the frame rate before choosing it. This can prevent problems during post-editing and playback.
5. Actual testing: Finally, don't forget to actually test. Before buying a camera, try shooting some videos at different frame rates to see which one best suits your needs. This will help you better understand the impact of frame rate on the picture and make a more informed choice.