On the Packet Loss Mechanism And Causes In Industrial Cameras
Industrial cameras play a crucial role in machine vision systems. However, during high-frequency image capture, users often encounter anomalies such as black bars, tearing, and misalignment in images. The essence of these issues is typically closely related to data packet loss during image transmission.
Ⅰ. Association Between Image Tearing/Black Bars and Packet Loss
Common Phenomena:
• Images appear fragmented, torn, or misaligned;
• Black stripes or horizontally discontinuous areas appear on images;
• Images display stuttering, screen corruption, or ghosting.
Most of these problems are related to a core technical issue—packet loss.

Ⅱ. What Is Packet Loss?—A Layman’s Analogy: The Courier Delivery System
This is a analogy model, compared the process of image capture and transmission to a courier company delivering packages:
• Image data packets = Courier packages
• Interrupts/network transmission = Delivery vehicles
• CPU/memory cache = Package sorting staff
• Image display = Customer receipt and unpacking
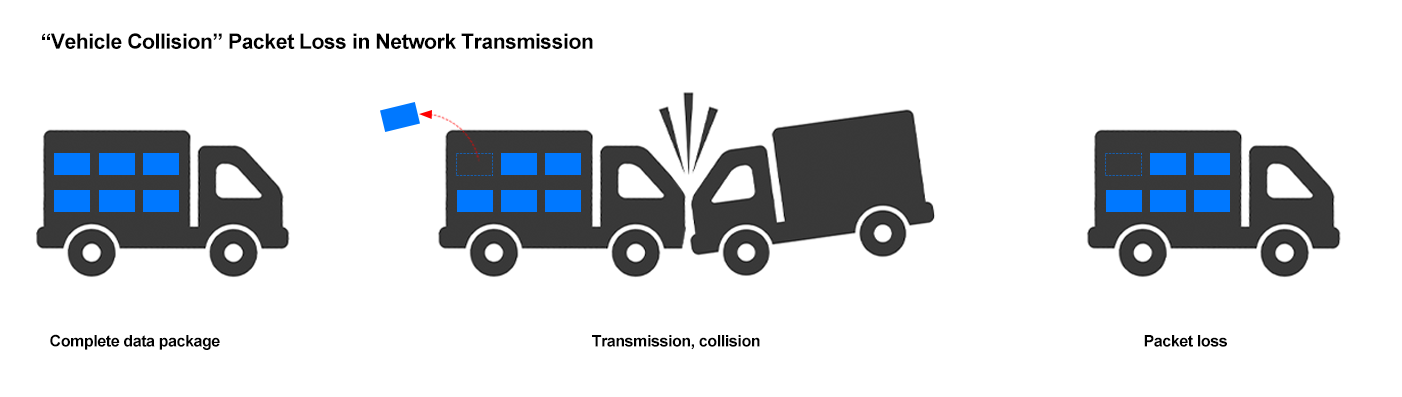
1. “Vehicle Collision” Packet Loss in Network Transmission
In traditional GigE port solutions, industrial cameras continuously split image data into multiple small packets and send them to the computer’s network card via Ethernet. This is similar to a company using many small vehicles to transport packages, with each vehicle carrying very little and frequently entering and exiting highways (interrupts):
• If the transportation frequency is too high, vehicles are prone to collide (interrupt congestion);
• Collisions cause some packages to fall (data loss);
• The result is black bars, tearing, and misalignment in images.
This situation is particularly common during high-speed capture, high-resolution imaging, or multi-camera synchronous acquisition.
2. CPU Overload: “Discarding Packages While Unpacking”
Another form of packet loss occurs during data reassembly. After the image data reaches the host, these “courier packages” need to be reassembled into a complete image:
• This is similar to a courier company sorting scattered packages for users;
• If the sorting staff (CPU/memory processing logic) is too busy or responds slowly;
• Excess packages are discarded as “garbage data”;
• As a result, the reassembled image lacks some “packages”—tearing and black bars occur again.
Ⅲ. Review of Common Technical Causes
|
Cause |
Description |
Analogy Explanation |
|
Insufficient Network Bandwidth |
Gigabit bandwidth is fully occupied or congested, causing data blockage |
Road too narrow, too many vehicles, prone to collisions |
|
Frequent Network Interrupts |
Slow system response to interrupt handling |
Vehicles collide, packages fall to the ground |
|
CPU Processing Bottleneck |
Untimely image sorting, memory cache overload |
Sorting staff too tired, misplace packages |
|
Lack of Jumbo Frame |
Default MTU too small, increasing the number of packets |
One vehicle can only carry one package, inefficient |
|
Poor Cables/Interference |
Signal attenuation, jitter, interference, etc. |
Packages damaged or lost during transportation |
Ⅳ. Solutions and Suggestions
1. Hardware Optimization
• Use Gigabit or 10-Gigabit network cards and enable Jumbo Frame (e.g., 9KB);
• Use high-quality, well-shielded network cables and keep the length within a reasonable range;
• Upgrade CPU, memory, or use edge computing gateways to alleviate processing pressure.
2. Software Configuration and System Optimization
• Properly configure the buffer size of the image acquisition SDK;
• Avoid running multi-threaded high-load tasks while capturing images;
• Enable hard interrupt binding and optimize IRQ Affinity settings;
• Use dedicated industrial real-time operating systems or Linux kernels with scheduling optimization.
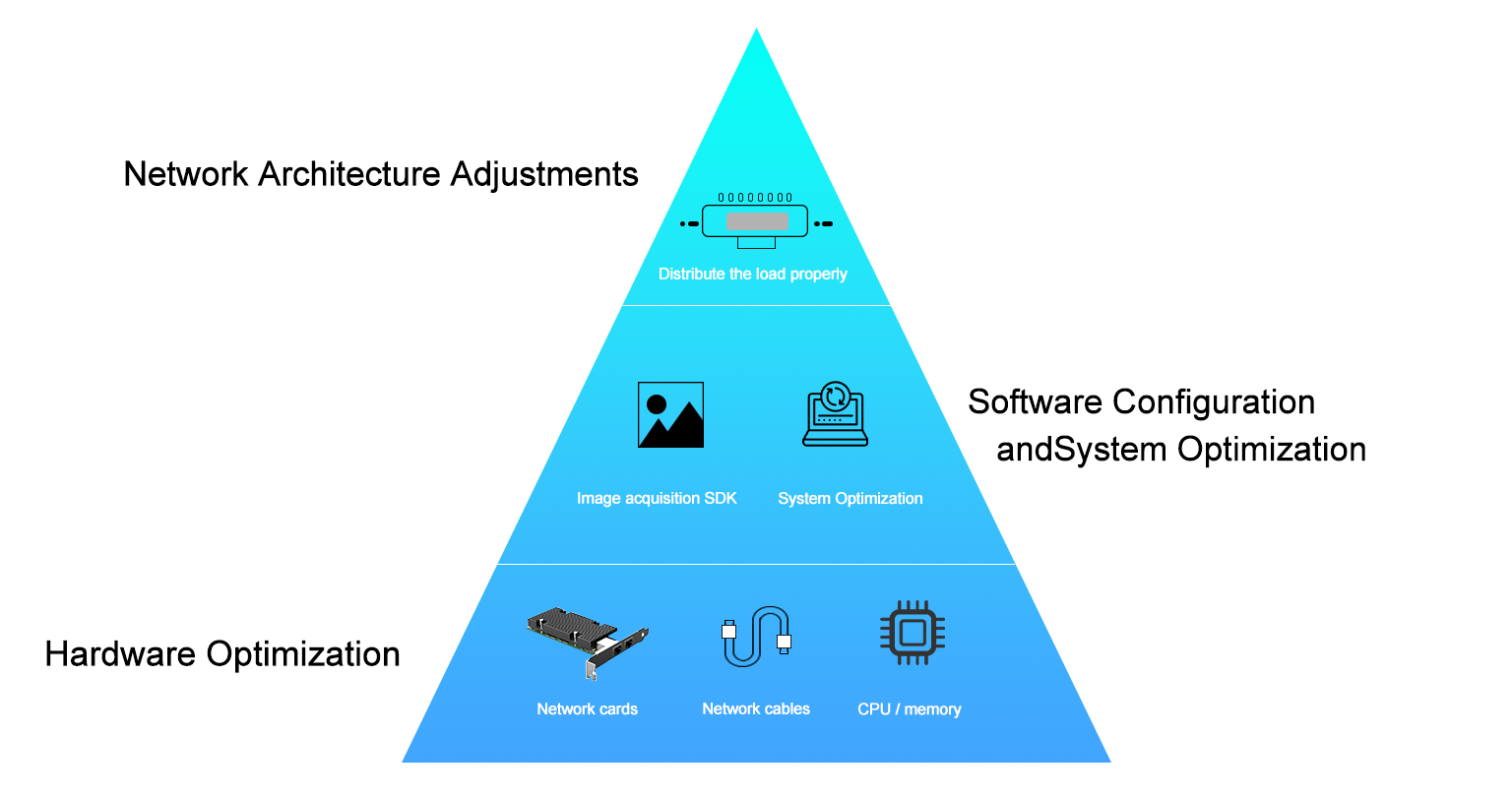
3. Network Architecture Adjustments
• Directly connect cameras or use switches supporting QoS;
• Reduce unnecessary network device nodes;
• Implement reasonable load distribution when deploying multiple cameras.
V. Conclusion
Issues such as black bars, tearing, and misalignment in industrial camera images are essentially caused by packet loss during image acquisition and transmission. Whether due to network congestion or host processing bottlenecks, the “courier delivery system” analogy provides an intuitive way to understand the root cause.
From “vehicle collisions” to “packages being mistakenly discarded,” these analogies vividly reflect the vulnerabilities of image acquisition systems under high-load conditions. Through hardware optimization, software scheduling, and network adjustments, such anomalies can be significantly reduced, enhancing the stability and reliability of image acquisition.