Smart Cameras in Machine Vision
In the realm of industrial automation and precision inspection, machine vision systems have emerged as indispensable tools. Among the key components of these systems, smart cameras are playing an increasingly pivotal role. This article delves into the distinctions between smart cameras and conventional industrial cameras, and explores two prominent applications of smart cameras in machine vision.
Differences from Conventional Industrial Cameras
Integration Level
Conventional industrial cameras are often just one part of a larger machine vision setup. They are mainly responsible for capturing images, and then these images need to be transferred to an external processing unit, such as a PC, for further analysis. This requires additional components like image acquisition cards and complex cabling to connect the camera to the processing device.
In contrast, smart cameras are highly integrated systems. They combine image acquisition, processing, and in some cases, even communication functions within a single compact unit. This integration not only simplifies the overall system architecture but also reduces the need for extensive external hardware, making them more space - efficient and easier to deploy in various industrial settings.
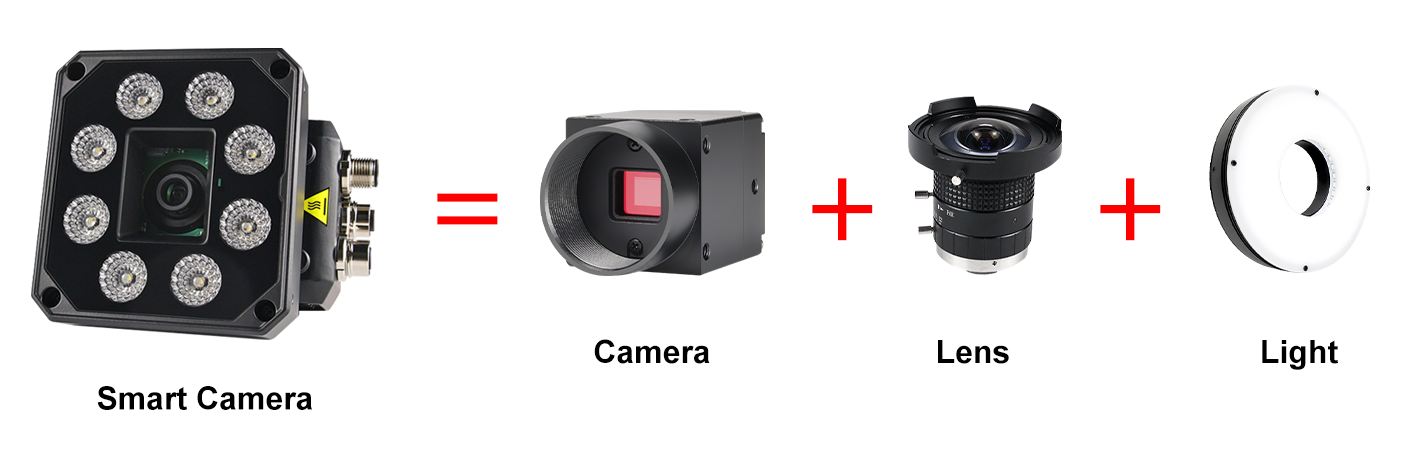

Processing Capability
Industrial cameras typically rely on the computing power of an external computer to perform tasks like image analysis, feature extraction, and decision - making. The camera captures the raw image data, and the processing software installed on the PC uses algorithms to interpret this data. This setup may face challenges in terms of processing speed, especially when dealing with high - resolution images or real - time applications, as the data transfer between the camera and the PC can be a bottleneck.
Smart cameras, on the other hand, are equipped with on - board processors. These processors can range from powerful digital signal processors (DSPs) to specialized vision processing units. With built - in processing capabilities, smart cameras can analyze the captured images immediately. They are capable of performing complex tasks such as pattern recognition, barcode reading, and defect detection in real - time, without the need to wait for data to be sent to and processed by an external device. This real - time processing ability makes smart cameras more responsive and suitable for applications where quick decision - making is crucial.
Ease of Use
Setting up a machine vision system with a conventional industrial camera often requires a certain level of technical expertise. The user needs to configure not only the camera settings such as exposure time, gain, and resolution but also install and set up the appropriate image processing software on the PC. Additionally, ensuring proper communication between the camera and the PC through the correct installation of drivers and network settings can be a complex process.
Smart cameras, however, are designed with user - friendliness in mind. They usually come with intuitive software interfaces that allow operators with little to no prior machine vision knowledge to easily configure the camera for their specific applications. Many smart cameras offer pre - programmed functions and templates for common tasks, such as object inspection or code reading. This simplicity of use makes smart cameras accessible to a wider range of industries and users, including small and medium - sized enterprises that may not have a dedicated team of machine vision experts.

Applications of Smart Cameras
Quality Control in Manufacturing
One of the most common applications of smart cameras in machine vision is in quality control within the manufacturing industry. For example, in the production of electronic components, smart cameras are used to inspect the soldering quality of circuit boards. The camera captures high - resolution images of the soldered joints, and its on - board processing unit analyzes these images in real - time. Using advanced pattern recognition algorithms, the smart camera can quickly identify defects such as misaligned solder joints, insufficient solder, or solder bridges.
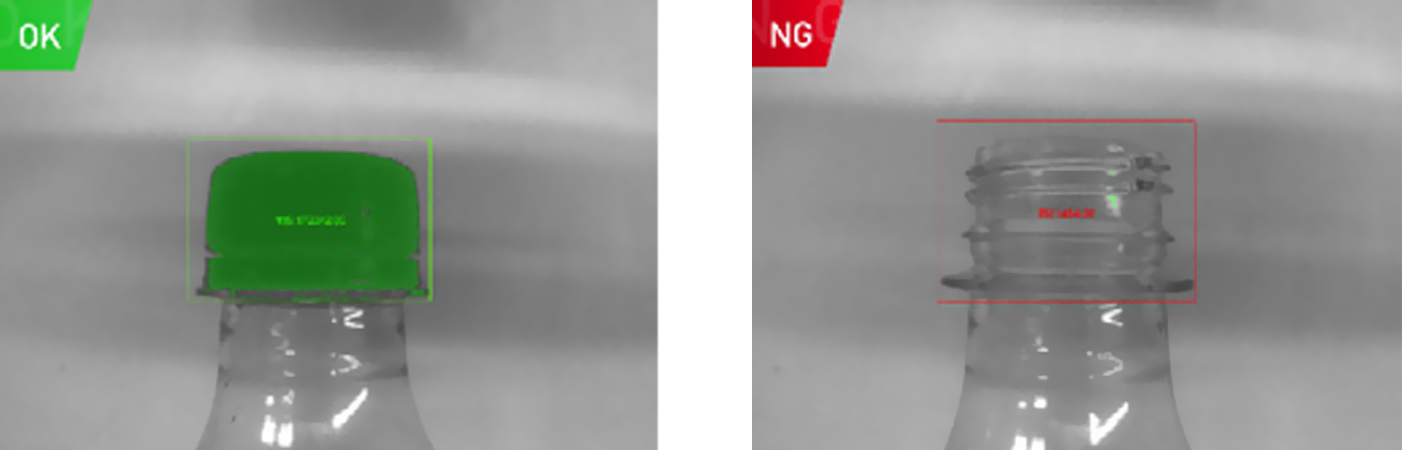
In a food and beverage factory, smart cameras are employed to check the integrity of product packaging. They can detect if a bottle cap is properly sealed, if labels are correctly applied, or if there are any visible defects in the packaging material. By continuously monitoring the production line, smart cameras ensure that only products meeting the highest quality standards are released for distribution, reducing the risk of defective products reaching the market and minimizing costly recalls.

Logistics and Warehouse Management
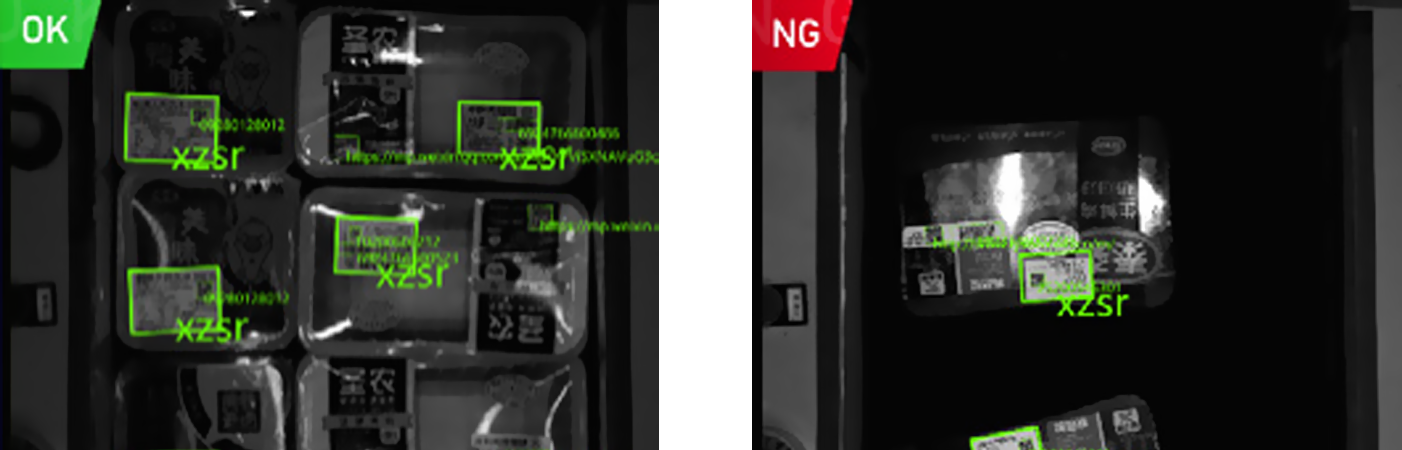
Smart cameras are also revolutionizing logistics and warehouse management. In large distribution centers, they are used for barcode and QR code reading on packages. As packages move along conveyor belts, smart cameras capture images of the codes and instantly decode the information. This enables accurate tracking of inventory, efficient sorting of packages, and seamless integration with the overall warehouse management system.

Another application in logistics is in autonomous guided vehicles (AGVs). Smart cameras are installed on AGVs to help them navigate through the warehouse environment. The cameras capture images of the surrounding area, and the on - board processing unit analyzes these images to detect obstacles, identify pathways, and ensure safe movement. This visual guidance system allows AGVs to operate more efficiently and safely, improving the overall productivity of the warehouse.
In conclusion, smart cameras offer distinct advantages over conventional industrial cameras in terms of integration, processing power, and ease of use. Their applications in machine vision, such as in quality control and logistics, are transforming various industries by enabling more efficient, accurate, and automated processes. As technology continues to advance, smart cameras are expected to play an even more significant role in the future of industrial automation and beyond.