What Are the Differences Between Object-Space Telecentric, Image-Space Telecentric, and Double-Sided Telecentric Lenses?
When it comes to precision in machine vision, the right lens can make or break your application. Telecentric lenses are the unsung heroes of industries like manufacturing, metrology, and quality control, delivering distortion-free imaging that ensures accuracy down to the smallest detail. But with options like object-space telecentric, image-space telecentric, and double-sided telecentric lenses, how do you choose the right one?
In this blog post, we’ll break down their differences, spotlight their strengths, and guide you to the perfect pick for your needs. Let’s dive into the world of telecentric lenses and bring your vision into focus!
What Is a Telecentric Lens?
Telecentric lenses are specialized optics designed to eliminate perspective distortion—a common headache in standard lenses where objects appear smaller as they move farther away. By keeping light rays parallel, telecentric lenses ensure that an object’s size stays consistent, no matter its distance from the lens (within the depth of field). This makes them indispensable for tasks requiring pinpoint accuracy, like measuring tiny parts or inspecting surfaces for defects.
The magic lies in how they handle light: some control it on the object side, others on the image side, and some do both. That’s where object-space, image-space, and double-sided telecentric lenses come into play. Let’s explore each type step-by-step.
Object-Space Telecentric Lenses: Precision Where It Starts
How They Work
Object-space telecentric lenses make light rays parallel on the object side. Only rays perpendicular to the lens from the object are captured, wiping out perspective errors. Whether an object shifts closer or farther within the depth of field, its size in the image remains unchanged.
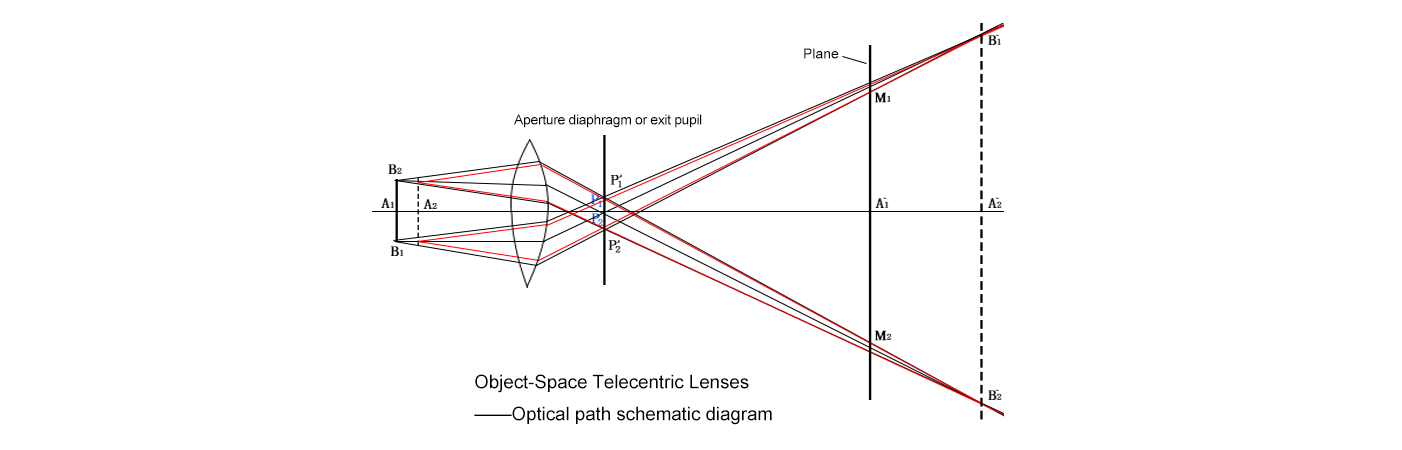
Key Advantages
- Stable Magnification: No need to recalibrate when objects move slightly—size stays consistent.
- Low Distortion: Great for flat or near-flat surfaces with minimal depth variation.
- Budget-Friendly: Typically more affordable than their double-sided counterparts.
Best Use Cases
- Measuring the diameter of screws or washers with unwavering accuracy.
- Inspecting flat surfaces like glass panels for scratches or blemishes.
- Aligning components precisely on an assembly line.
The Trade-Off
Since they only control the object side, image-side imperfections like slight blurring or vignetting can creep in if the sensor isn’t perfectly aligned. For many tasks, though, this is a minor hiccup.
Image-Space Telecentric Lenses: Clarity Where It Lands
How They Work
Image-space telecentric lenses flip the script, making light rays parallel on the image side. This ensures rays hit the camera sensor straight-on, boosting sharpness and reducing optical quirks across the entire field of view.
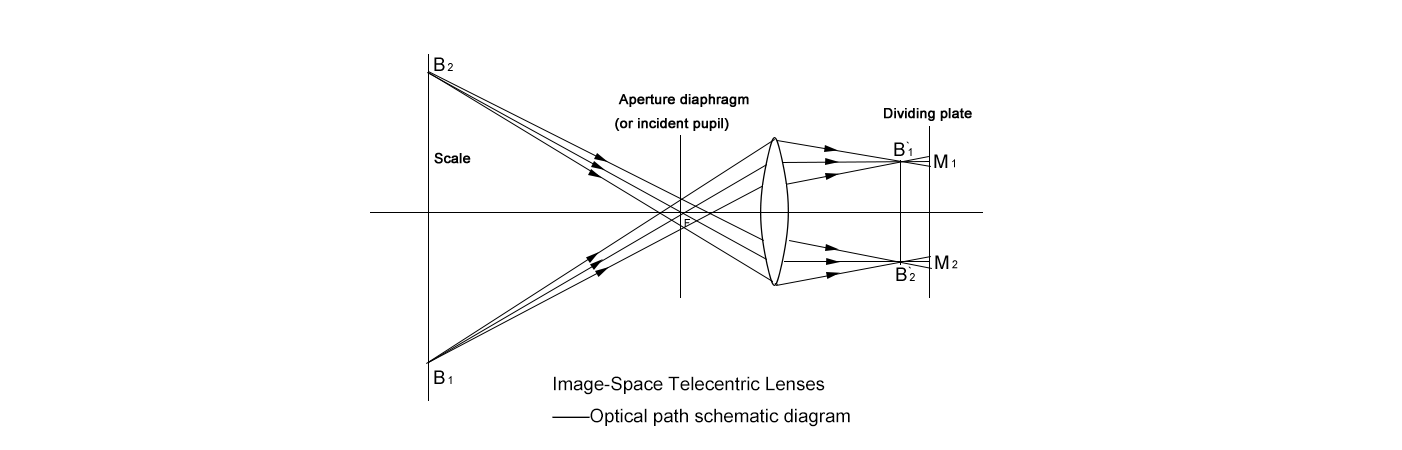
Key Advantages
- Even Illumination: Consistent lighting from edge to edge, perfect for texture or color analysis.
- Reduced Aberrations: Sharp, clear images with minimal distortion.
- Sensor-Friendly: Excels with larger sensors, maintaining quality corner-to-corner.
Best Use Cases
- Capturing fine details in semiconductor inspection or microscopy.
- Analyzing colors accurately for sorting or grading tasks.
- Imaging larger objects where uniformity is a must.
The Trade-Off
They don’t manage the object side, so perspective distortion can sneak in if objects vary in distance. This makes them less ideal for precision measurements across depth changes.
Double-Sided Telecentric Lenses: The Ultimate Precision Package
How They Work
Double-sided (or bi-telecentric) lenses pull off the ultimate feat: parallel light rays on both the object and image sides. This dual control delivers top-tier precision and image quality, no compromises.
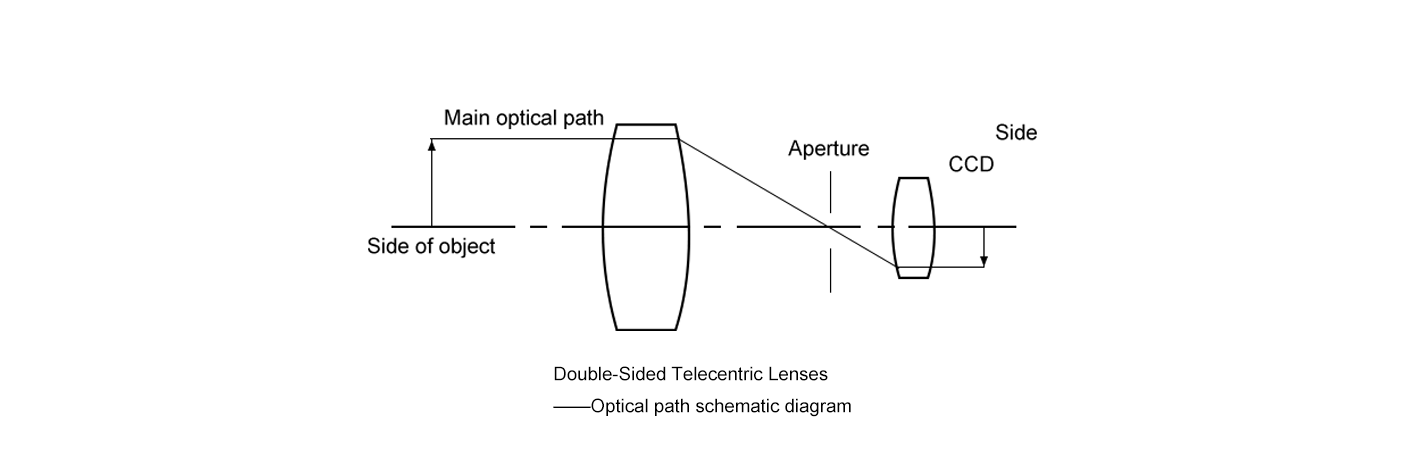
Key Advantages
- Zero Perspective Error: Size stays rock-solid, and distortion vanishes.
- Unmatched Consistency: Ideal for measurements requiring sub-micron precision.
- Wide Depth of Field: Stays sharp over greater distances, simplifying setups.
Best Use Cases
- Measuring intricate parts like gears or turbine blades with extreme accuracy.
- Reconstructing 3D models for volumetric analysis or reverse engineering.
- Inspecting high-stakes products in aerospace or medical device manufacturing.
The Trade-Off
Perfection comes at a cost—literally. These lenses are pricier, bulkier, and may need more setup time. They’re overkill for simpler jobs where single-sided telecentricity does the trick.
Seeing the Difference
Picture a grid of squares viewed through each lens:
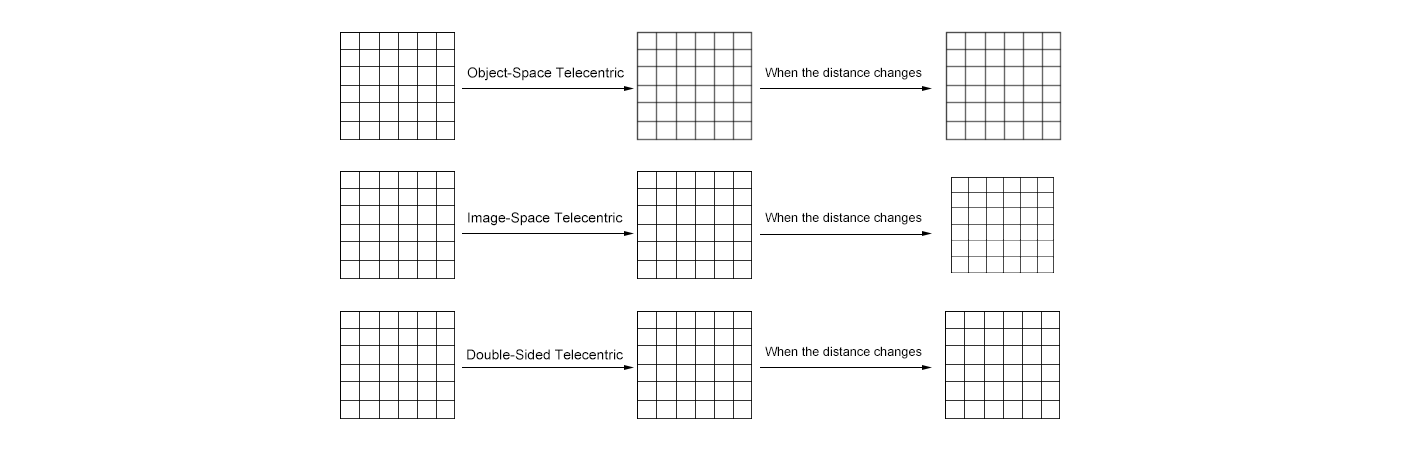
- Object-Space Telecentric: Squares stay the same size but might blur slightly at the edges.
- Image-Space Telecentric: Squares are razor-sharp but could resize with distance shifts.
- Double-Sided Telecentric: Squares are perfectly sized and crystal-clear, no matter where they sit.
This visual snapshot shows why matching the lens to your task is key.
Picking the Right Lens for You
Here’s a quick guide to match your needs:
- Prioritize Measurement Accuracy? Go for object-space or double-sided telecentric lenses to lock in size consistency.
- Need Top-Notch Image Quality? Choose image-space or double-sided telecentric lenses for sharpness and uniformity.
- Watching the Budget? Start with object-space telecentric lenses for a solid mix of precision and value.
- Demand the Best? Invest in double-sided telecentric lenses when precision is everything.
Think about your application’s distortion tolerance, object size, and budget. Still unsure? Testing lenses or chatting with a machine vision pro can seal the deal.
Why Telecentric Lenses Are a Game-Changer
Sure, telecentric lenses cost more upfront, but their payback is huge:
- Pinpoint Accuracy: Say goodbye to measurement errors from perspective distortion.
- Reliable Results: Perfect for automated inspections that need repeatability.
- Time Savings: Less recalibration, fewer adjustments.
- Cost Efficiency: Fewer defects mean less rework down the line.
In precision-driven fields, they’re not just nice-to-have—they’re must-have.
Take Your Vision to the Next Level
The right telecentric lens can revolutionize your machine vision system, delivering the precision and clarity your project deserves. Whether it’s the measurement reliability of object-space lenses, the image perfection of image-space lenses, or the all-in-one power of double-sided lenses, there’s a fit for you.
Ready to sharpen your focus? Explore HIFLY telecentric lens lineup or reach out to our machine vision experts for tailored advice. Don’t let distortion cloud your goals—contact us today and see the difference precision makes!