How to Select Industrial Lenses
The selection of industrial lenses should be based on specific application scenarios, focusing on the matching of the following key parameters and requirements:
1. Clarify core requirements
Inspection target: Size (e.g., high resolution is required for tiny parts), features (e.g., edge detection is sensitive to distortion).
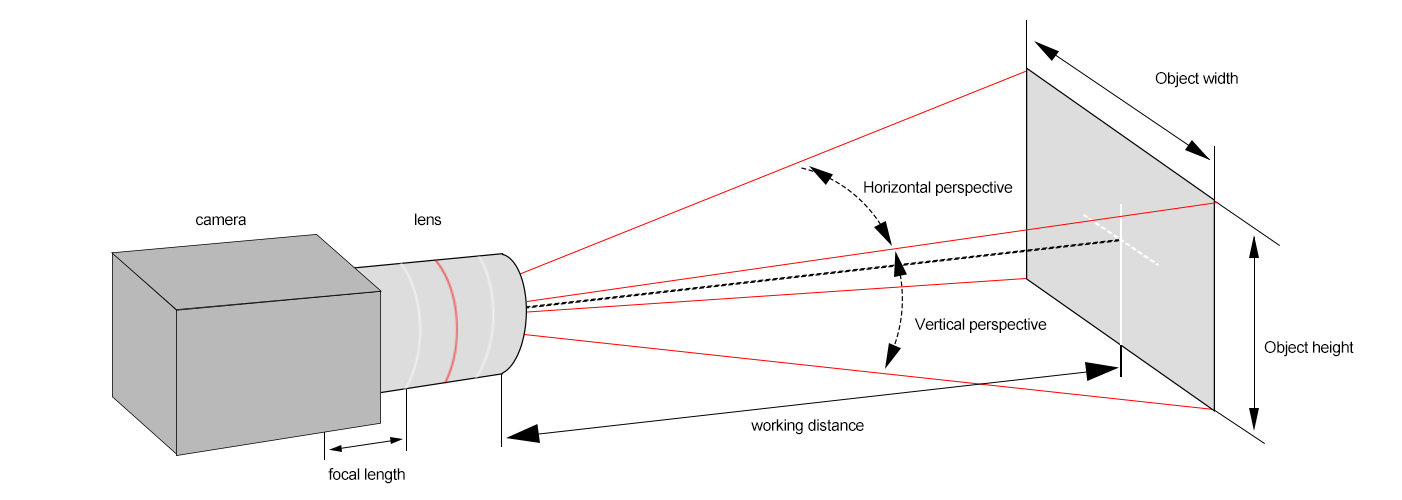
Working distance: The distance from the lens to the object, which affects the type of lens (e.g., telecentric lenses are suitable for long working distances).
Field of View (FOV): It needs to cover the inspection area. The calculation formula is: FOV = sensor size × working distance / focal length.
2. Match sensor parameters
Sensor size: The imaging circle of the lens must cover the sensor (e.g., a 1-inch sensor requires a corresponding lens support) to avoid vignetting.
Pixel size: The lens resolution must match the sensor pixels. The formula is: lens resolution (line pairs/mm) ≈ 1/(2 × pixel size (mm)) to ensure no waste of pixels.
3. Key lens parameters
Focal length: The shorter the focal length, the larger the field of view; conversely, the higher the magnification (under the same working distance).
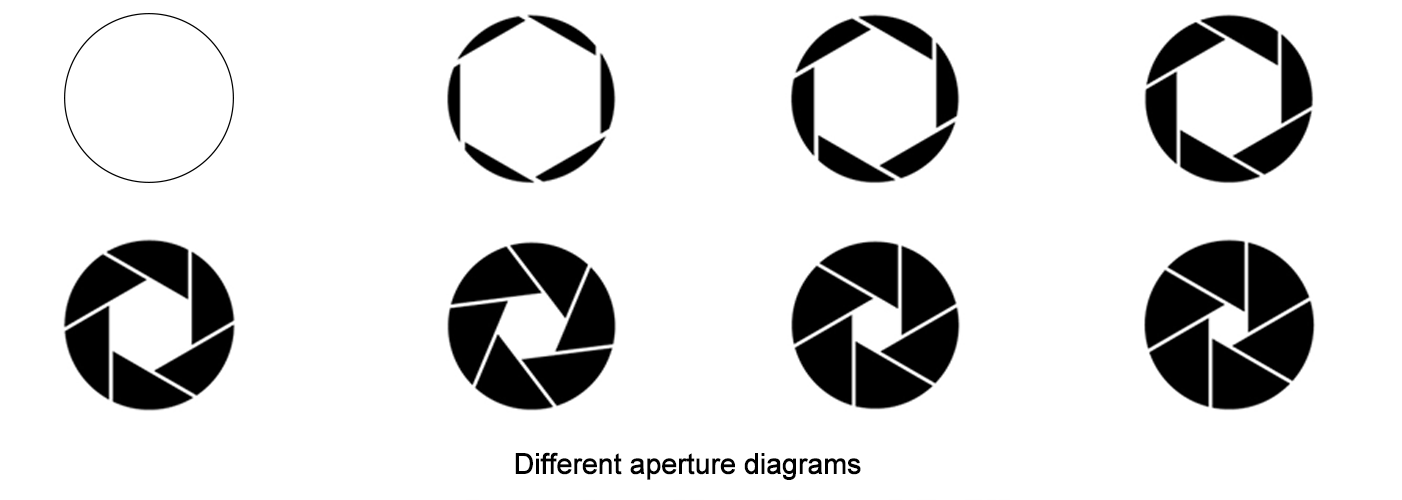
Aperture: A large aperture (small F-value) allows more light, suitable for low-light environments but with a small depth of field; a small aperture has a large depth of field, suitable for scenarios requiring a wide clear range.
Distortion: Low distortion is required when detecting size and position (e.g., telecentric lenses have minimal distortion), and it can be appropriately relaxed for appearance inspection.
Depth of field: The range where objects can be clearly imaged before and after, which is related to the aperture, focal length, and working distance (a small aperture, short focal length, and long working distance result in a larger depth of field).
4. Requirements for special scenarios
Moving objects: Choose high-frame-rate lenses to avoid motion blur.
Harsh environments: Choose industrial-grade lenses that are dust-proof, waterproof, and temperature-resistant.
Multispectral inspection: The lens must support the corresponding wavelength (e.g., infrared lenses).
By gradually matching the above parameters, the selection range can be narrowed down, and finally, the appropriate lens can be determined based on brand reliability and cost.