Key Features of High-Quality Line Scan Camera Lenses
Understanding the Role of Line Scan Camera Lenses in Industry
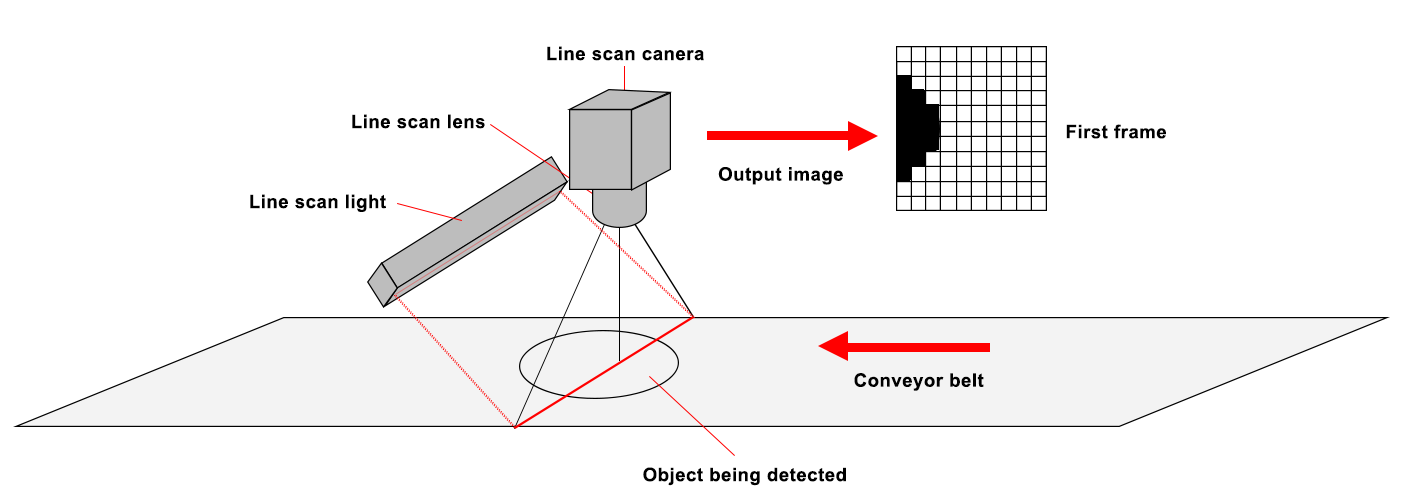
In advanced machine vision applications, line scan cameras are essential for capturing high-resolution, continuous images of moving objects. From quality inspection in electronics to print verification in packaging and defect detection in textiles, the accuracy of these systems depends heavily on the lens used. A high-quality line scan camera lens doesn’t just magnify an image—it ensures precision, sharpness, and consistent performance across the full width of the scan. In industrial settings where defects measured in microns can have significant implications, the right lens selection is critical.
Optical Precision and Resolution
One of the most important features of a high-quality line scan camera lens is optical precision. In line scan imaging, the camera captures one line of pixels at a time, and these lines are stitched together to form a complete image. Any optical distortion or chromatic aberration will be repeated across the entire scan, leading to inaccuracies. Therefore, lenses must be designed to maintain sharpness and clarity from the center to the edges of the field of view. The resolution of the lens should also match or exceed that of the camera’s sensor to avoid underutilizing its capabilities.
Minimal Distortion for Accurate Measurements
In industries such as PCB inspection, document scanning, and high-speed sorting, even a small amount of distortion can cause measurement errors. High-quality line scan camera lenses are engineered to minimize geometric distortions—such as barrel or pincushion effects—across the entire image. This ensures that the scanned data accurately reflects real-world dimensions, which is crucial for applications involving dimensional checks, barcode reading, or pattern matching.
Uniform Illumination and Image Brightness
A lens should deliver uniform brightness from edge to edge, especially in applications where consistent lighting is challenging. Variations in brightness can cause false positives or missed defects during automated inspection. High-quality lenses use advanced coatings and optical designs to minimize vignetting and ensure even light transmission, which in turn supports reliable image processing.

Robust Build Quality for Industrial Environments
Industrial line scan systems often operate in environments with dust, vibration, or fluctuating temperatures. High-quality line scan lenses are constructed with durable materials, sealed housings, and precise mechanical tolerances. Metal barrels, reinforced mounts, and temperature-resistant optics ensure that the lens maintains alignment and optical integrity even under demanding conditions. Some lenses are also designed with anti-reflective or scratch-resistant coatings to prolong operational life.
Compatibility with Sensors and Cameras
A top-performing lens must be optimized for the specific sensor size and pixel pitch of the camera it serves. Using a lens that isn’t matched to the sensor can cause issues such as reduced resolution, light falloff, or image artifacts. Manufacturers often provide specifications indicating the optimal sensor size and camera model for each lens. For example, a lens designed for a 16k-pixel line scan sensor must maintain high resolution and sharpness across the entire 80 mm or wider field of view without losing detail.
Wide Aperture and Adjustable Focus
A wide aperture allows more light into the camera, enabling faster scan speeds and improved image quality in low-light conditions. Many high-quality lenses also feature adjustable focus mechanisms, allowing operators to fine-tune sharpness for specific working distances. In automated production lines where object sizes or conveyor positions may vary, this flexibility can greatly enhance system performance.

Low Chromatic Aberration for Color Accuracy
In color line scan systems—such as those used in printing, packaging, and food inspection—chromatic aberration can cause color fringing or misalignment between the red, green, and blue channels. High-quality line scan lenses use specialized glass types and optical designs to minimize this effect, ensuring accurate color reproduction and consistent results.
Ease of Integration and Maintenance
Industrial environments demand efficiency not only in operation but also in installation and upkeep. A high-quality line scan camera lens should be easy to integrate into existing systems, with standard mount types (such as F-mount, M42, or M72) and compatibility with common optical accessories. Additionally, the lens design should allow straightforward cleaning and recalibration without requiring complete system disassembly.
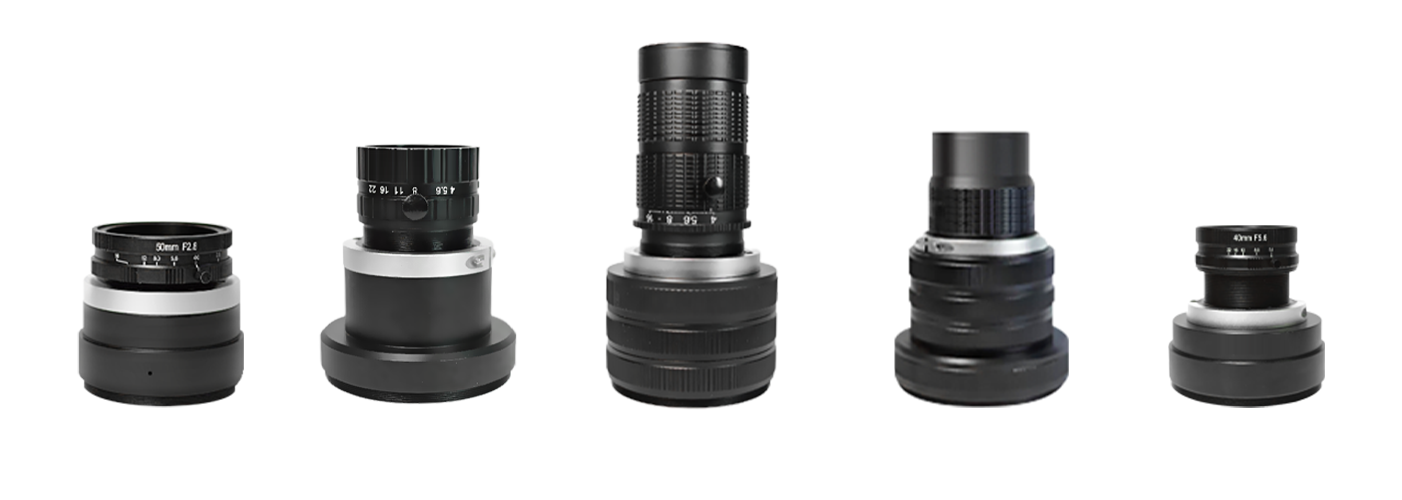

Future Trends in Line Scan Lens Technology
As industrial imaging moves toward higher resolutions, faster scan rates, and more compact systems, lens technology is evolving. Lenses with apochromatic correction, improved anti-reflective coatings, and compact yet rugged housings are becoming more common. Additionally, AI-enhanced imaging systems may soon rely on lenses with embedded sensors to monitor optical performance and signal when recalibration or replacement is needed.
Conclusion
Choosing the right line scan camera lens is a critical decision that impacts the accuracy, efficiency, and reliability of an industrial imaging system. High-quality lenses offer superior optical precision, minimal distortion, uniform illumination, and robust durability—ensuring that the camera’s capabilities are fully utilized. Whether in high-speed printing inspection, semiconductor manufacturing, or logistics automation, investing in the best possible lens ensures consistent performance and long-term operational stability. By understanding these key features, engineers and decision-makers can select lenses that deliver both technical excellence and economic value.